Federal E-Verify program 2025: Eliminate Guesswork
Your Guide to Employment Verification
The Federal E-Verify program is a web-based system that allows employers to confirm their employees’ eligibility to work in the United States by matching Form I-9 information against government records.
Quick Facts About the Federal E-Verify Program:
- What it is: Internet-based employment verification system run by DHS and SSA
- Purpose: Confirms work authorization by checking government databases
- Results: Provides answers in 3-5 seconds with 98.88% approval rate
- Requirements: Mandatory for federal contractors, varies by state for other employers
- Process: Used after Form I-9 completion, within 3 business days of hire
If you’re an HR manager drowning in compliance paperwork and worried about hiring mistakes, you’re not alone. The employment verification process has gotten more complex over the years, but it doesn’t have to be overwhelming.
E-Verify works as a companion to Form I-9, not a replacement. After your new employee completes their I-9 form, you enter their information into the E-Verify system. The system then checks this data against records from the Department of Homeland Security and Social Security Administration.
The system gives you one of several results: Employment Authorized (you’re good to go), Tentative Nonconfirmation (the employee needs to resolve a mismatch), or in rare cases, Final Nonconfirmation (employment cannot be confirmed).
Over 700,000 employers used E-Verify as of 2018, and that number keeps growing as more states require it and businesses recognize its value for maintaining legal workforces.
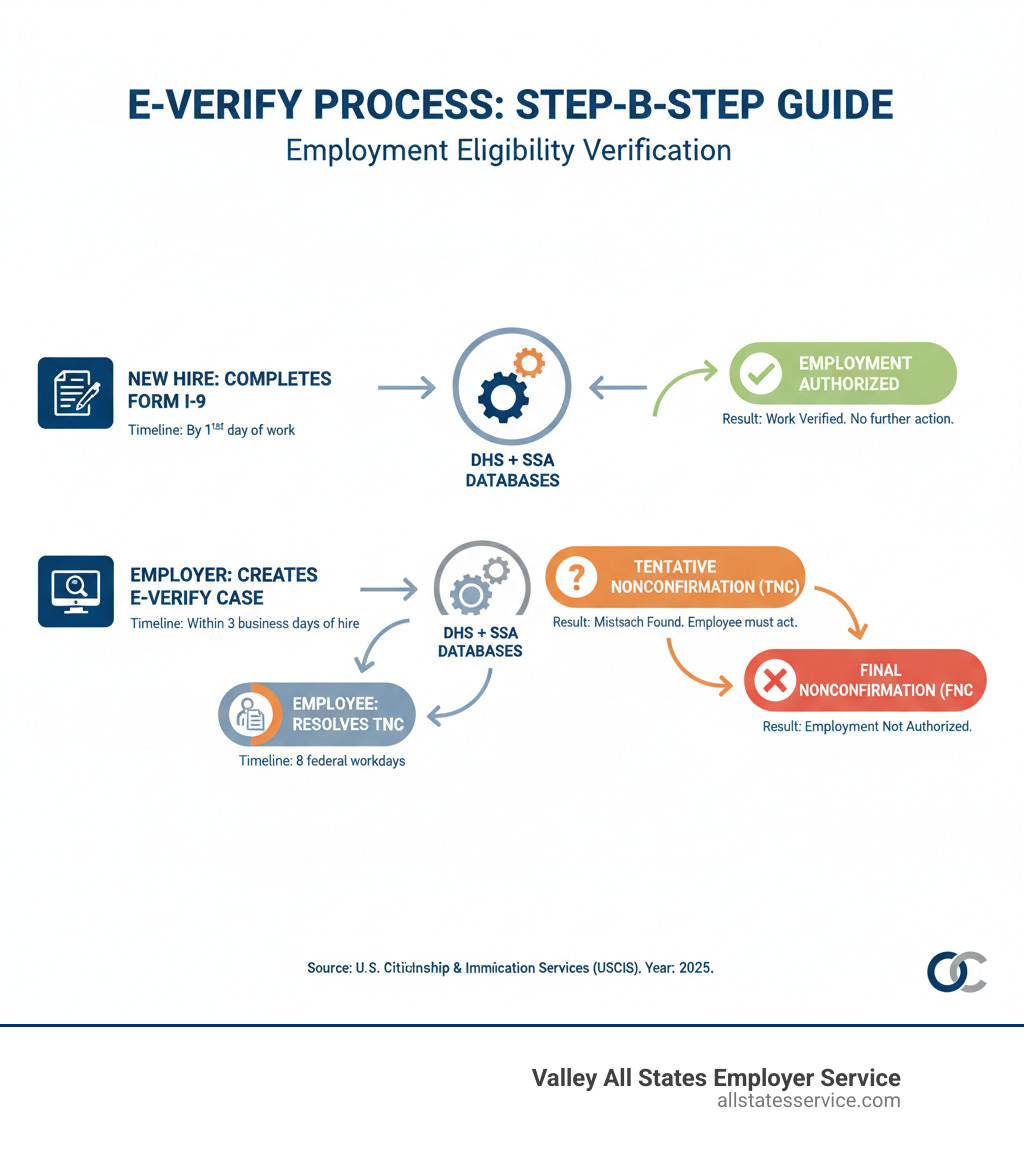
What is E-Verify and How Does It Relate to Form I-9?
At its core, the Federal E-Verify program is an internet-based system operated by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) in partnership with the Social Security Administration (SSA). Its primary goal is simple: to allow employers to electronically confirm the employment eligibility of their newly hired employees. Think of it as a digital handshake between your new hire’s information and vast government databases.
How does this digital handshake happen? It all starts with Form I-9, the Employment Eligibility Verification form. This form is a fundamental requirement for all U.S. employers, citizens and non-citizens alike. It verifies an individual’s identity and their authorization to work in the United States. E-Verify then takes the information from a completed Form I-9 and electronically compares it against records available to the DHS and SSA. This process helps ensure that every employee you hire is legally authorized to work.
We often hear questions about whether E-Verify replaces Form I-9. The answer is a clear no. E-Verify is a powerful tool that supplements the Form I-9 process. It improves the accuracy and integrity of employment eligibility verification, but it doesn’t eliminate the need for the physical or electronic completion and retention of the Form I-9 itself. For more detailed information on how these two critical components work together, you can explore our guide on E-Verify and I-9.

The E-Verify Process Explained
Let’s walk through the E-Verify process step-by-step. It’s designed to be straightforward, delivering results quickly.
- Form I-9 Completion: First, the new employee accepts a job offer and completes Section 1 of Form I-9, attesting to their work authorization. They then present acceptable documents (from Lists A, B, or C) to you, their employer, who completes Section 2.
- Case Creation: Once the Form I-9 is complete, you, the employer, must create a case in the E-Verify system. This must be done within three business days of the employee’s first day of employment. You’ll input the employee’s information directly from their Form I-9 into the E-Verify system.
- System Check: E-Verify then electronically sends this information to both DHS and SSA databases. It’s looking for a match between the provided data and the records held by these agencies.
- Case Results: Most of the time, the system provides a result within three to five seconds. The most common result, and what we all hope for, is “Employment Authorized.” This means the employee’s information matched government records, and they are authorized to work. In fact, as of 2018, 98.88% of E-Verify applicants were approved to work, indicating a high success rate for authorized individuals.
However, sometimes the system returns a “Tentative Nonconfirmation” (TNC) or, less frequently, a “Final Nonconfirmation.” These results require further action and understanding.
Understanding Tentative Nonconfirmations (TNCs)
A Tentative Nonconfirmation (TNC), also known as a “mismatch,” means that the information entered into E-Verify did not immediately match records available to the DHS or SSA. A TNC does not mean the individual is unauthorized to work. It simply means there’s a discrepancy that needs to be resolved.
What causes a TNC?
- Data entry errors (a typo by the employer or employee).
- Name changes not updated with SSA or DHS.
- Citizenship or immigration status changes not updated.
- Records not correctly updated in government databases.
When an employee receives a TNC, they have specific rights. You, as the employer, must:
- Inform the employee of the TNC result immediately.
- Print the “Further Action Notice” from E-Verify and provide it to the employee.
- Give the employee the opportunity to contest the TNC, typically within eight federal government workdays.
- Not take any adverse action against the employee (e.g., delaying training, reducing pay, terminating employment) solely because of the TNC while they are attempting to resolve it.
If the employee chooses to contest the TNC, they will follow the instructions on the “Further Action Notice” to contact the relevant agency (SSA or DHS) to resolve the discrepancy. Once the employee contacts the agency, the E-Verify system will update with a new status. If the issue is resolved, the case will eventually result in “Employment Authorized.” If the employee does not contest the TNC, or if they contest it and the issue cannot be resolved, the case will result in a “Final Nonconfirmation,” meaning their work authorization could not be confirmed.
It’s important to us that employers handle TNCs correctly to protect employee rights and avoid potential legal issues. For more insights into TNCs and E-Verify accuracy, consider this Fact Sheet on E-Verify Error Rates. The U.S. government reported that as of May 2023, out of 48,042,413 cases, 738,507 resulted in mismatches, but only a tiny fraction (0.011%) of those contested mismatches were not eventually confirmed. This highlights that most TNCs are resolvable.
Navigating the Federal E-Verify Program: Who is Required to Participate?
While the Federal E-Verify program is voluntary for many employers, it’s mandatory for others. Understanding whether your business falls into the mandatory category is critical for compliance. The requirements can stem from federal contracts, state laws, or even municipal ordinances.
Generally, employers who are not federal contractors or subject to state or local mandates can choose to participate in E-Verify voluntarily. However, the landscape is constantly shifting, with more jurisdictions adopting mandatory E-Verify laws. To get a comprehensive understanding of the varying requirements, we recommend reviewing our E-Verify State Laws Complete Guide.
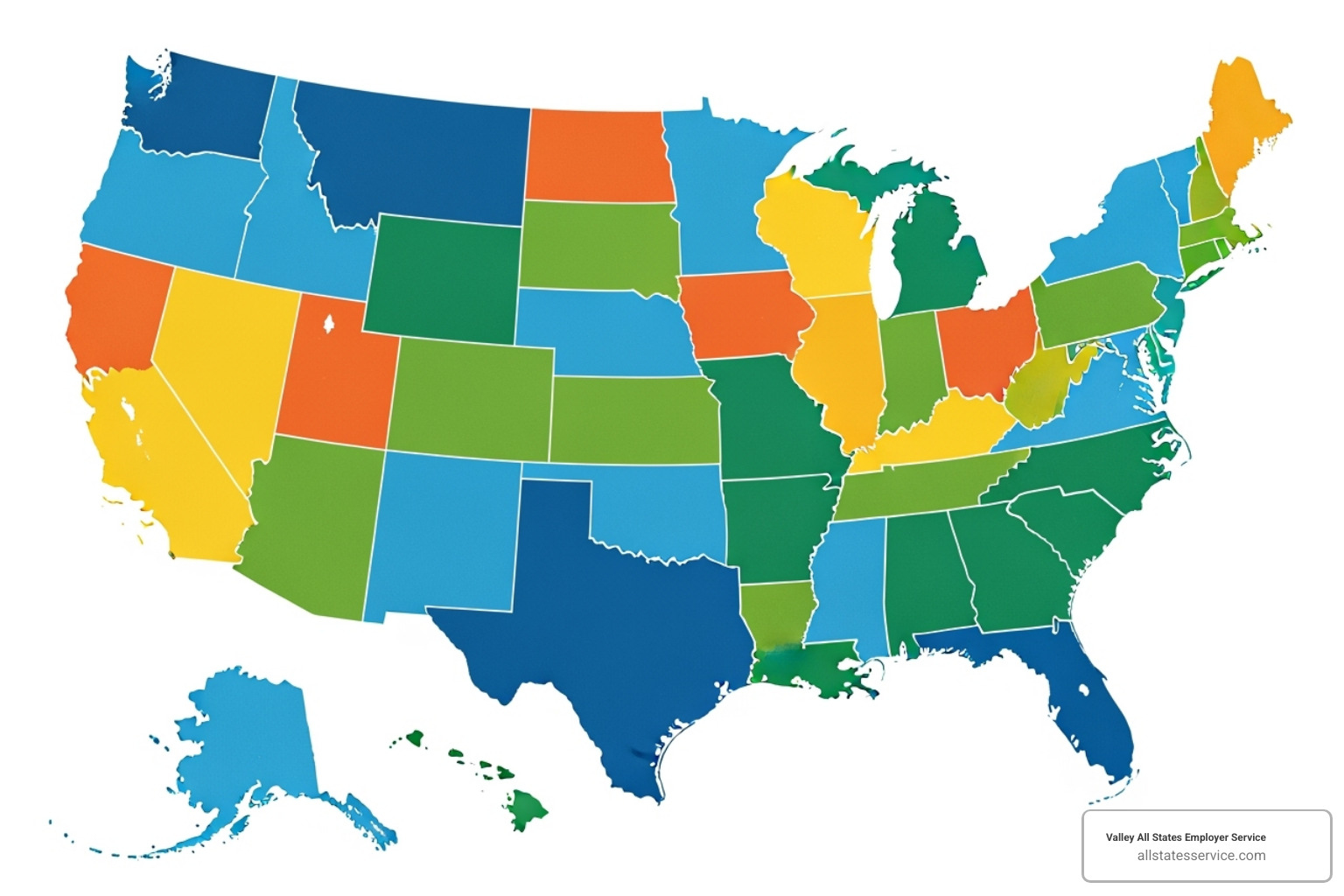
Federal Contractor Requirements
One of the most significant drivers of mandatory E-Verify participation comes from federal contracts. If your business holds a federal contract that includes the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) E-Verify clause, then participation in the Federal E-Verify program is not optional—it’s a requirement.
The DHS started requiring all federal contractors and vendors to use E-Verify in August 2007. This mandate applies to:
- New Hires: All employees hired by the federal contractor, regardless of whether they work directly on the federal contract, must be run through E-Verify.
- Existing Employees Assigned to the Contract: Employees who are already on your payroll but are subsequently assigned to a federal contract containing the FAR E-Verify clause must also be verified.
There are specific rules and responsibilities for federal contractors, including posting E-Verify notices and adhering to strict timelines. We have a dedicated resource for this: E-Verify for Contractors. Ensuring compliance in this area is paramount to maintaining your federal contracts and avoiding severe penalties.
State-by-State E-Verify Mandates
Beyond federal requirements, a complex web of state and local laws dictates E-Verify usage. Many states have taken it upon themselves to mandate E-Verify for employers within their borders, creating a patchwork of requirements that can be challenging to steer, especially for businesses operating across multiple states.
These state mandates can vary significantly:
- Universal Mandates: Some states require all or most private employers to use E-Verify for all new hires. Examples include Alabama, Arizona, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, and Utah.
- Public Employer Mandates: Many states, such as Colorado, Idaho, Indiana, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, Oklahoma, Pennsylvania, Texas, and Virginia, require their state agencies, public employers, and/or state contractors to use E-Verify.
- Business License Requirements: In some instances, E-Verify compliance might be tied to obtaining or maintaining a business license.
- Local/Municipal Requirements: Even if a state doesn’t have a universal mandate, individual cities or counties might have their own ordinances requiring E-Verify.
The penalties for non-compliance with state E-Verify laws can range from fines to the suspension or revocation of business licenses. It’s a dynamic area of law, with new legislation frequently being proposed or enacted. Therefore, staying informed about the specific requirements in each state where you operate is essential.
Benefits, Penalties, and Common Criticisms
The Federal E-Verify program, like any major government initiative, comes with a set of advantages, potential pitfalls, and areas of concern. For employers, understanding these aspects helps in making informed decisions about participation and compliance.
The Advantages of Using E-Verify
Why would an employer voluntarily choose to use E-Verify, or why is it beneficial where mandated? The benefits are clear, especially for businesses committed to maintaining a legal workforce.
- Legal Workforce Assurance: E-Verify provides a quick and effective way to confirm that your employees are authorized to work in the U.S., significantly reducing the risk of inadvertently hiring unauthorized workers. This helps you maintain a compliant workforce and avoid legal liabilities.
- Reduced Paperwork Errors: By electronically cross-referencing information, E-Verify helps catch potential errors or inconsistencies that might be missed in a manual Form I-9 review.
- Improved Reputation: Demonstrating a commitment to legal employment practices can improve your company’s reputation as a responsible employer.
- Free Government Service: For employers, the E-Verify system itself is free to use, making it an accessible tool for compliance.
- High Accuracy: The system boasts a high accuracy rate. As we mentioned, 98.88% of E-Verify applicants were approved to work as of 2018, showing its effectiveness in confirming eligibility for the vast majority.
We believe that leveraging E-Verify can be a significant asset to your HR and compliance strategy. Dive deeper into these advantages by checking out our page on the Benefits of E-Verify.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
Ignoring E-Verify requirements or mismanaging the Form I-9 process can lead to serious consequences. The penalties for non-compliance are designed to be a deterrent and can be costly for businesses.
- Fines for Form I-9 Errors: Even administrative errors on Form I-9 can result in significant fines. These can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars per violation, depending on the nature and extent of the errors.
- Penalties for Knowingly Hiring Unauthorized Workers: If you are found to have knowingly hired or continued to employ an unauthorized worker, the penalties are far more severe. These can include substantial fines, and in egregious cases, criminal charges.
- Debarment from Federal Contracts: For federal contractors, non-compliance with the FAR E-Verify clause can lead to debarment, meaning your company could lose its eligibility to bid on or receive future federal contracts. This can be a devastating blow for businesses reliant on government work.
- State-Specific Penalties: As discussed, many states have their own E-Verify mandates with corresponding penalties, which can include fines, suspension of business licenses, or even criminal charges for repeated violations.
The financial and reputational risks associated with non-compliance are substantial. It’s not just about avoiding fines; it’s about safeguarding your business’s future.
Criticisms and Concerns Surrounding E-Verify
Despite its benefits, the Federal E-Verify program has faced its share of criticism and raised several concerns among various groups. We think it’s important to acknowledge these perspectives to provide a balanced view.
- Data Accuracy and TNC Impact: While the system is highly accurate, critics point to the potential for database errors leading to Tentative Nonconfirmations for authorized workers. Even a small percentage of errors can affect thousands of individuals, causing stress and potential loss of employment while they resolve the issue.
- Potential for Discrimination: Some worry that E-Verify could lead to discriminatory practices, where employers might selectively verify employees or mistakenly assume a TNC indicates unauthorized status without allowing the employee to resolve it.
- Privacy Issues: Concerns have been raised about the vast amount of personal data collected and stored by the government for E-Verify purposes, and the potential for misuse or security breaches.
- Identity Theft Vulnerabilities: Sophisticated identity thieves can sometimes bypass the system by using stolen identities that appear valid in government databases.
These criticisms highlight the ongoing need for program refinement, robust employee protections, and transparent data management. While E-Verify is a powerful tool, it’s not without its challenges, especially for small businesses trying to steer complex regulations. We offer insights specifically for E-Verify for Small Businesses to help address these concerns.
The Evolution of E-Verify: History, Updates, and What’s Next
The Federal E-Verify program isn’t a static system; it has a rich history of evolution and continuous updates aimed at improving its functionality and security. Understanding its journey helps us appreciate where it stands today.
A Brief History of the Federal E-Verify Program
The origins of E-Verify trace back to the Illegal Immigration Reform and Immigrant Responsibility Act (IIRIRA) of 1996. This act authorized the creation of pilot programs to test electronic employment verification. What we know today as E-Verify officially began as the Basic Pilot Program.
- 1996: IIRIRA authorized pilot programs for electronic employment verification.
- 1997: The Basic Pilot Program was launched, initially limited to a few states.
- Early 2000s: The program gradually expanded, demonstrating its potential for broader application.
- August 2007: A significant milestone occurred when the DHS mandated that all federal contractors and vendors include the E-Verify FAR clause in their contracts, making participation compulsory for a large segment of employers.
- 2008: The program was renamed E-Verify and was made available to employers in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, Guam, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and the Commonwealth of Northern Mariana Islands.
This journey from a small pilot to a nationwide program underscores the government’s commitment to ensuring a legal workforce. You can explore a more detailed timeline on the History and Milestones of E-Verify page.
Latest Features and Updates to the Federal E-Verify Program
The E-Verify system is constantly being improved to improve user experience, security, and efficiency. We are always keeping up with these changes to ensure our clients benefit from the most current practices.
- E-Verify+: This is a major recent improvement, designed to streamline the employment eligibility verification process even further. E-Verify+ promises innovation, protection, convenience, transparency, and efficiency, making the system more user-friendly and robust. For a closer look at what this means for you, we encourage you to watch the webinar on Introducing E-Verify+.
- New Reporting Tool: A valuable addition for employers, this tool allows users to generate a Status Change report. This report helps identify cases affected by parole terminations and Employment Authorization Document (EAD) revocations, providing crucial insights for managing your workforce’s eligibility.
- Login.gov Security Integration: To improve account security and user authentication, E-Verify is requiring users to create a Login.gov account to access their E-Verify accounts. This move aligns with broader government efforts to centralize and secure online services.
- Alternative Procedures for Remote I-9 Verification: In a significant update, effective August 1, 2023, the DHS authorized alternative procedures for examining Form I-9 documents. This means that employers enrolled in E-Verify who meet certain criteria can now remotely examine employee documentation, a crucial development for remote hiring practices. This flexibility is a direct response to evolving work environments and a testament to the program’s adaptability.
These updates reflect a commitment to modernizing the Federal E-Verify program and making it more responsive to the needs of employers while maintaining the integrity of employment verification.
Simplify Your Compliance and Eliminate the Guesswork
Navigating the complexities of the Federal E-Verify program, alongside state-specific mandates and Form I-9 requirements, can feel like a daunting task. The administrative burden and the constant worry about compliance risks can divert valuable time and resources away from what you do best: running your business.
We understand these challenges intimately. That’s why Valley All States Employer Service specializes in providing outsourced E-Verify workforce eligibility verification. Our mission is to simplify this intricate process for employers like you, ensuring accuracy and efficiency every step of the way. We act as your expert, impartial, and efficient E-Verify Employer Agent, minimizing errors and administrative headaches.
With our team by your side, you can eliminate the guesswork from your employment verification process. We ensure that your Form I-9s are carefully completed and that E-Verify cases are processed correctly and on time, keeping you compliant with federal and state regulations. Imagine the peace of mind knowing that your workforce eligibility is handled by experts, allowing you to focus on growth and innovation.
Ready to transform your E-Verify compliance from a source of stress into a streamlined, worry-free process? Let us help you steer the ever-changing landscape of employment eligibility verification.
Learn more about our comprehensive E-Verify & I-9 Compliance solutions today!