Small business I-9: 3-Day Guide to Hassle-Free Hiring
Why Small Business I-9 Compliance Matters More Than Ever
Small business I-9 requirements might feel like just another piece of paperwork, but they’re actually a critical legal obligation that protects your business from devastating fines and legal trouble. Every employer in the United States must complete Form I-9 for every new hire to verify their identity and work authorization, no exceptions.
Here’s what you need to know about Small business I-9 compliance:
- The Form: Employment Eligibility Verification (Form I-9) is required by federal law for all employees hired after November 6, 1986
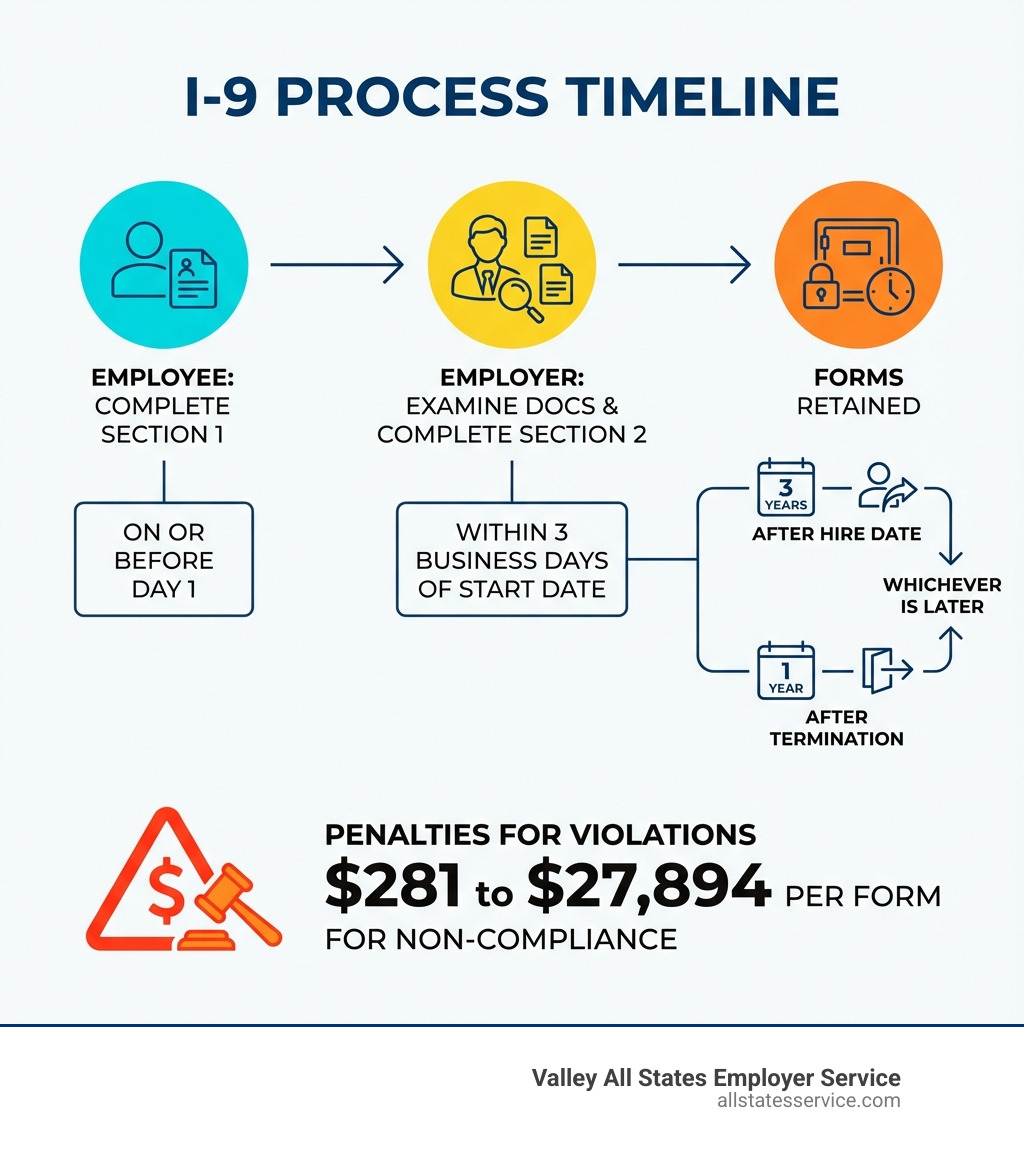
- The Timeline: Employees complete Section 1 on or before their first day; employers must complete Section 2 within 3 business days
- The Penalty: Fines range from $281 to $27,894 per form for violations
- The Documents: Employees must present original documents from List A (identity + work authorization) OR List B (identity) + C (work authorization)
- The Retention: Keep forms for 3 years after hire date or 1 year after termination, whichever is later
Here’s a reality check: 44% of businesses are planning to expand their teams in 2025. That means more hiring, more I-9 forms, and more opportunities for costly mistakes if you’re not prepared.
The good news? Once you understand the process, I-9 compliance becomes straightforward. You don’t need to be an immigration attorney or HR expert to get it right.
This guide walks you through everything from the basics of what Form I-9 actually is, to handling tricky situations like remote employees, to avoiding the common mistakes that trigger audits. We’ll also show you how to store your forms correctly and when you might want to consider using E-Verify.
Running a small business comes with enough challenges. Let’s make sure I-9 compliance isn’t one of them.
Basic Small business I-9 vocab:
What is Form I-9 and Why Is It So Important for Your Business?
When you bring a new team member on board, you’re not just gaining an employee, you’re also taking on a few crucial responsibilities. One of the most important is ensuring they are legally authorized to work in the United States. That’s where Form I-9, also known as the Employment Eligibility Verification form, comes in.
This form is a cornerstone of federal law, required for every employer in the U.S., regardless of size. It helps us verify both an employee’s identity and their legal authorization to work. Whether you’re hiring a U.S. citizen or a non-citizen, the Form I-9 process is mandatory. It’s not just about bureaucracy, it’s about protecting your business from significant legal and financial risks.
The Legal Foundation of Form I-9
The legal obligation to complete Form I-9 stems from the Immigration Reform and Control Act (IRCA) of 1986. This federal law mandates that all employers, including small businesses, verify the identity and employment authorization of all new hires. Failure to comply can lead to substantial penalties and legal consequences, which we’ll dig into shortly.
Essentially, Form I-9 ensures we maintain a legal workforce, safeguarding your business against audits, fines, and reputational damage. It’s a critical component of responsible hiring practices. To get a clear picture of what this form entails, you can explore our detailed guide on What is an I-9?. The USCIS (U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services) outlines these requirements, emphasizing that every employer who recruits, refers for a fee, or hires an individual for employment in the U.S. must complete Form I-9. You can find more direct information on the USCIS requirement.
I-9 vs. W-9: What’s the Difference?
A common point of confusion for small business owners is distinguishing between Form I-9 and Form W-9. While both are crucial for different aspects of hiring and contracting, they serve distinct purposes.
- Form I-9: This is all about employment eligibility verification. We use it to confirm that an individual is authorized to work in the U.S. and to verify their identity. It’s exclusively for employees.
- Form W-9: This form, officially titled “Request for Taxpayer Identification Number and Certification,” is used to obtain the correct name and Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) of U.S. persons, like independent contractors, for tax reporting purposes. It doesn’t verify work authorization.
The key distinction lies in the worker’s classification: employee versus independent contractor. If you hire an employee, you need an I-9. If you engage a true independent contractor, you’ll need a W-9. Misclassifying workers can be a significant audit risk, so understanding this difference is vital for your Small business I-9 compliance efforts.
The Step-by-Step I-9 Completion Process for Small Businesses
Navigating the Form I-9 process doesn’t have to be overwhelming. It’s a two-section form with clear responsibilities for both the employee and the employer. The most critical aspect is adhering to deadlines, as even minor delays can lead to compliance issues. For a comprehensive overview, check out our Employment Eligibility Verification Complete Guide.
Step 1: Employee Completes Section 1
This is the employee’s part of the process, and it’s essential they complete it accurately and on time.
- What to do: The employee fills out their personal information, such as their full legal name, address, date of birth, and Social Security Number. They must also attest to their citizenship or immigration status by checking one of the boxes provided.
- When to do it: This section must be completed and signed by the employee no later than their first day of employment for pay. It’s important to remember they should not complete it before accepting a job offer.
- Preparer/Translator: If someone helped the employee complete Section 1, that person must also complete the Preparer and/or Translator Certification (Supplement A) on the form.
Accuracy here is paramount, as errors in Section 1 can lead to technical violations. Our guide on I-9 Form Completion offers more in-depth advice.
Step 2: Employer Completes Section 2
Once Section 1 is done, the ball is in our court as the employer. This section requires careful attention to detail and a strict adherence to timelines.
- What to do: We, or our authorized representative, must physically examine the original documents the employee presents to establish both their identity and employment authorization. We then record details from these documents on the form.
- When to do it: This crucial step must be completed and signed by us within three business days of the employee’s first day of employment for pay. If an employee works for less than three business days, Section 2 must be completed no later than their first day of employment.
- Document Examination: We must examine the actual, original documents. Photocopies are not acceptable for this step. We then record the document title, issuing authority, document number, and expiration date (if any) in Section 2.
- Signature: Finally, we sign and date Section 2, certifying that we have examined the documents and that they appear to be genuine and relate to the employee.
We cannot tell an employee which specific documents to provide, only that they must choose from the acceptable lists. For more details on our responsibilities, refer to Filling out an I-9 Employer.
Step 3: Understanding Acceptable Documents (Lists A, B, and C)
The documents employees can present for Form I-9 verification are categorized into three lists: List A, List B, and List C. We need to understand these lists thoroughly to ensure proper compliance.

- List A Documents: These documents establish both identity and employment authorization. An employee presenting one List A document has fulfilled both requirements.
- Examples: U.S. Passport or Passport Card, Permanent Resident Card (Form I-551), Foreign Passport with a temporary I-551 stamp or printed notation, Employment Authorization Document (Form I-766).
- List B Documents: These documents establish identity only.
- Examples: Driver’s license or ID card issued by a state or outlying possession of the U.S., School ID card with a photograph, Voter’s registration card, U.S. Military card or draft record.
- List C Documents: These documents establish employment authorization only.
- Examples: Social Security card (unrestricted), Certification of Birth Abroad (Form FS-545 or DS-1350), Original or certified copy of a birth certificate, Native American tribal document.
Employees have the right to choose which acceptable documents they present from these lists. We cannot request specific documents. They can provide either one document from List A OR one document from List B and one document from List C. For a complete list and further guidance, you can always refer to the official Learn about acceptable I-9 documents and our own I-9 Document Requirements Complete Guide.
Navigating Common Small Business I-9 Challenges
Running a small business means we’re often juggling many tasks, and I-9 compliance can sometimes feel like an added burden. However, being aware of common pitfalls and taking proactive steps can save us a lot of headaches, and money, down the road. Our HR Compliance for Small Business guide provides broader insights.
One significant challenge is avoiding discrimination claims. We must not ask for specific documents, nor can we treat employees differently based on their citizenship, immigration status, or national origin. This includes the risk of “over-documentation,” where we ask for more documents than legally required, which can be seen as discriminatory.
The High Cost of Non-Compliance: Penalties and Risks
The stakes for Small business I-9 compliance are incredibly high. The government takes these requirements seriously, and violations can lead to financially devastating penalties.

- Technical Violations: These are often clerical errors, like missing dates, signatures, or incorrect information in certain fields. Penalties for these can range from $281 to $2,789 for the first offense. While these might seem minor, they add up quickly, especially if we have multiple forms with errors.
- Substantive Violations: These are more serious, involving failures to complete sections, present documents, or follow proper verification procedures. Fines for substantive violations or uncorrected technical errors range from $288 to $2,861 per form.
- Knowing Violations: The most severe penalties are for “knowing violations,” which occur when we knowingly employ unauthorized workers. These fines can range from $698 to $5,579 for first offenses per unauthorized worker, escalating to $5,579 to $27,894 for second and subsequent offenses. In extreme cases, employing unauthorized workers can climb to $28,619 per person.
These penalties can be financially devastating for a small business. Government agencies like ICE (Immigration and Customs Enforcement) conduct audits, often with just three days’ notice. If we’re not prepared, the consequences can be severe. Understanding these risks is the first step in mitigating them. Our I-9 Compliance Penalties article offers a deeper dive, and you can learn more about what to expect during an inspection from Learn about the I-9 inspection process.
Handling I-9 Verification for Remote Employees
The rise of remote work has introduced unique challenges for I-9 compliance, particularly concerning the physical examination of documents in Section 2. We can’t always meet employees in person.
- Authorized Representative: One common solution is to designate an “authorized representative.” This can be anyone we authorize, such as a notary public, a trusted family member, or even a colleague, to physically examine the employee’s documents on our behalf and complete Section 2. We, as the employer, remain liable for any errors the representative makes, so clear instructions and training are crucial.
- Alternative Procedures: The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has also provided alternative procedures for remote document examination, especially in response to changing work environments. It’s vital to stay updated on the latest guidance from USCIS regarding these procedures.
Navigating remote I-9s requires careful planning to ensure compliance without causing undue burden on our remote workforce. Our resources on Remote Employee I-9 Verification and I-9 Verification Process for Remote Employees offer practical guidance.
Storing and Retaining I-9 Forms Correctly
Completing the Form I-9 is just half the battle. Proper storage and retention are equally important for Small business I-9 compliance.
- The “3-1 Rule”: We must retain completed I-9 forms for either three years after the date of hire or one year after the date the employee’s employment ends, whichever is later. This means we can’t just toss them when an employee leaves.
- Separate Storage: I-9 forms contain sensitive personal information, so they should be stored securely and separately from employee personnel files. This helps protect privacy and ensures easy access if an auditor requests them.
- Physical vs. Electronic: We can store I-9s either as physical paper copies or electronically. If we choose electronic storage, our system must comply with specific DHS standards for electronic generation, storage, and retention. Simply scanning and saving to a general email folder or filing cabinet isn’t enough; it needs to be a secure, compliant system.
- Audit Readiness: Maintaining organized records ensures we’re always ready for a potential audit. Government agencies can request to inspect our I-9 records with just three days’ notice. Having them readily accessible and correctly filed saves us stress and potential fines.
Your Go-To Resources for I-9 Compliance
Staying informed is our best defense against non-compliance. The rules and forms can change, so knowing where to find reliable guidance is key for Small business I-9 success.
- Official Government Resources: The USCIS website, particularly I-9 Central, is our primary source for official forms, instructions, and updates. The Employers Handbook for I-9 (M-274) is an invaluable, comprehensive guide that details every aspect of the I-9 process.
- Training: Whoever is responsible for completing and verifying I-9 forms in our company should be properly trained. USCIS offers free online training resources to help us get started.
- Self-Audits: Conducting periodic internal audits of our I-9 forms is a best practice. This allows us to catch and correct errors before a government audit does. It’s a proactive step that can save us thousands in penalties. For assistance with this, consider our I-9 Audit Services.
The Role of E-Verify for Small Business I-9 Compliance
While not mandatory for most small businesses, E-Verify is an optional, free online system that can add an extra layer of confidence to our employment eligibility verification process.
- What is E-Verify: E-Verify allows us to electronically confirm the employment eligibility of our new hires by comparing the information from their Form I-9 with records available to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security and the Social Security Administration.
- How it Works with Form I-9: E-Verify works in conjunction with Form I-9. After we complete the I-9, we then submit the employee’s information through the E-Verify system. It provides a quick response, often within seconds, indicating whether the employee is authorized to work.
- Benefits: For small businesses, E-Verify can help reduce the risk of unknowingly employing unauthorized workers, protecting us from significant penalties. It provides an official confirmation that goes beyond the visual inspection of documents.
If we’re considering adding E-Verify to our hiring process, our E-Verify Small Business Guide and E-Verify and I-9 resources can help us understand its benefits and implementation.
Simplify Your I-9 Process and Protect Your Business
As we’ve seen, Small business I-9 compliance is a non-negotiable aspect of hiring in the U.S. It protects us from hefty fines, legal complications, and ensures we maintain a legal workforce. While the process has specific steps and deadlines, it’s entirely manageable once we understand the requirements.
Key takeaways for your small business:
- Always use the latest version of Form I-9 from USCIS.
- Ensure employees complete Section 1 on or before their first day.
- Physically examine original documents and complete Section 2 within three business days.
- Never discriminate or ask for specific documents.
- Understand the “3-1 Rule” for retention and store forms securely and separately.
- Train anyone involved in the I-9 process.
- Consider internal audits or E-Verify for added protection.
Our goal at Valley All States Employer Service is to help small businesses like yours thrive by taking the burden of compliance off your shoulders. We understand that your focus should be on growth, not paperwork. With our expert, impartial, and efficient E-Verify and I-9 processing, we minimize errors and administrative headaches, providing you with peace of mind.
Ready to simplify your compliance and protect your business? Streamline your hiring with our E-Verify and I-9 Compliance services today.