I-9 audit penalties: Avoid Costly Fines in 2025
Why I-9 Compliance is More Critical Than Ever in 2025
I-9 audit penalties have reached unprecedented levels in 2025, with fines now ranging from $288 to $28,619 per violation. For HR managers and business owners, understanding these penalties is crucial for protecting your company from financial and legal risk.
Quick Answer: Current I-9 Penalty Ranges (2025)
| Violation Type | First Offense | Second Offense | Third+ Offense |
|---|---|---|---|
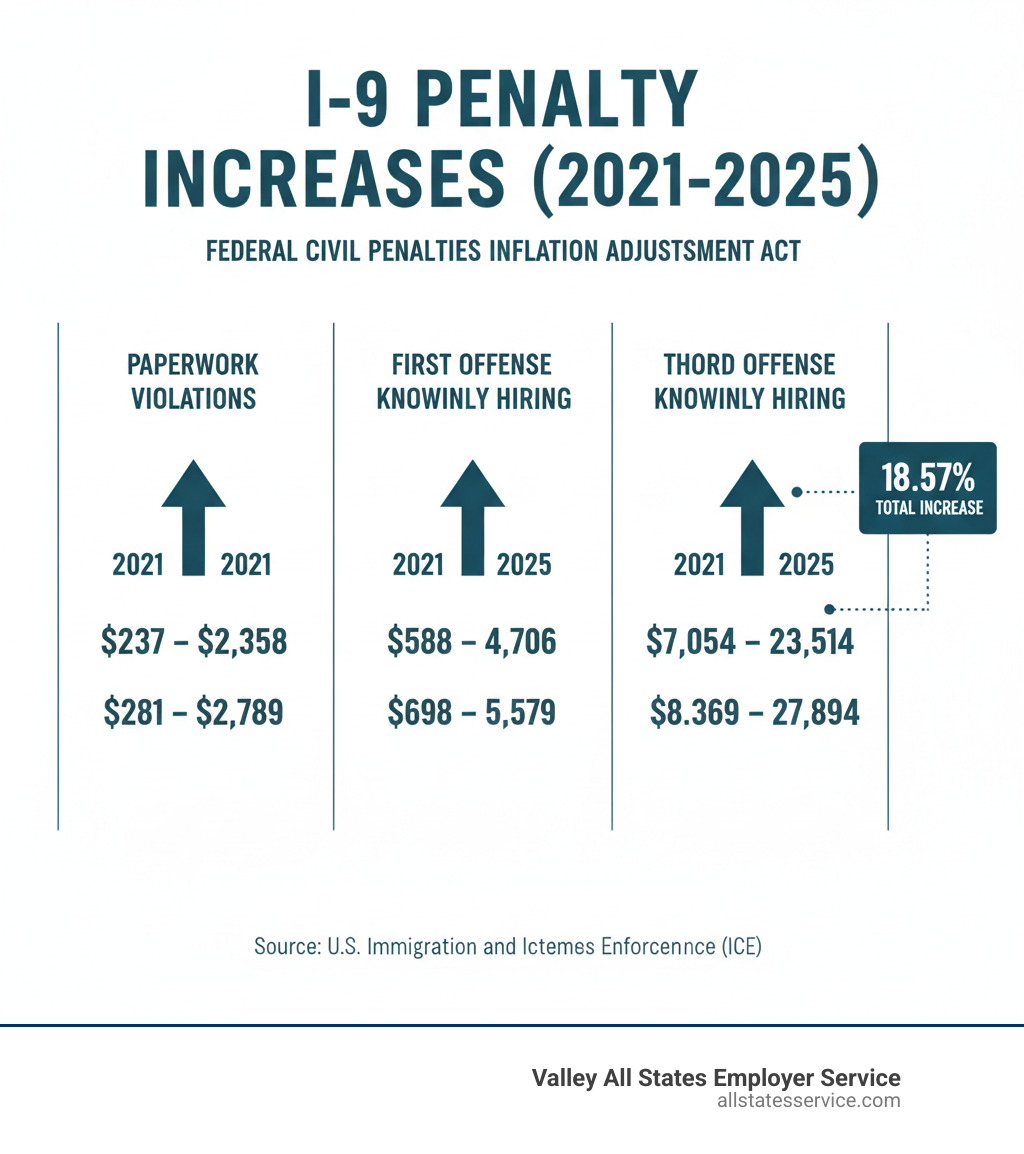
| Paperwork Violations | $281 – $2,789 per form | N/A | N/A |
| Knowingly Hiring Unauthorized Workers | $698 – $5,579 per worker | $5,579 – $13,946 per worker | $8,369 – $27,894 per worker |
| E-Verify Final Nonconfirmation Failure | $973 – $1,942 per employee | N/A | N/A |
| Document Abuse | $230 – $2,304 per violation | N/A | N/A |
The enforcement landscape has shifted dramatically. U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) increased I-9 audits from approximately 1,360 in fiscal year 2017 to nearly 6,450 in 2019. This trend continues in 2025, with immigration enforcement remaining a top priority.
What makes this particularly urgent? Three factors:
-
Automatic annual increases: The Federal Civil Penalties Inflation Adjustment Act mandates yearly penalty adjustments. Since December 2021, I-9 fines have increased by 18.57%.
-
No safe harbor for paperwork errors: Even if all your employees are legally authorized to work, simple paperwork mistakes like missing signatures or incomplete sections can trigger fines of hundreds or thousands of dollars per form.
-
Escalating penalties for repeat offenses: A third offense for knowingly hiring unauthorized workers can cost your business up to $27,894 per worker, potentially crippling smaller companies.
The challenge is that Form I-9, while seemingly simple, is a “tricky trap” for businesses. You must complete it for every employee hired after November 6, 1986, use the correct version, finish Section 2 within three business days, verify documents without discriminating, and retain forms for specific periods. Any misstep can lead to penalties escalating into five or six figures.
The good news is that I-9 compliance is manageable with the right systems. This guide explains I-9 penalties, how they are calculated, and how to avoid them.
Understanding the Full Spectrum of I-9 Penalties
I-9 audit penalties are more than a simple fine. The Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986 (IRCA) created a range of consequences, from civil fines and criminal charges to discrimination lawsuits. One misstep can have a cascading effect.
U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE), under the Department of Homeland Security (DHS), leads enforcement. The Department of Justice (DOJ) and the Department of Labor also play roles, focusing on different aspects of compliance.

Beyond fines, violations can lead to debarment from government contracts, back pay orders, and mandated hiring. The stakes are high.
Civil Monetary Penalties: From Paperwork Errors to Knowingly Hiring
Civil penalties are the most common type of I-9 audit penalties. They range from simple paperwork errors to knowingly hiring unauthorized workers, with a vast difference in severity.
Paperwork violations are a common trap. These include blank fields, missing signatures, missed deadlines (like completing Section 2 after three business days), using outdated forms, or failing to meet retention requirements. Even accepting an expired driver’s license can trigger a violation. Each error can result in a fine, even if all employees are authorized to work.
The government distinguishes between technical errors, which you can fix, and substantive violations. If you fail to correct technical errors within 10 business days of notification from ICE, they become substantive violations with higher penalties.
For 2025, each paperwork violation carries fines between $281 and $2,789 per form. An audit of 50 employees with multiple errors can quickly add up to a substantial bill. The Federal Register’s latest fine schedule details these numbers.
Knowingly hiring unauthorized workers is a major violation with a tiered system that punishes repeat offenders. A first offense costs $698 to $5,579 per worker. A second offense jumps to $5,579 to $13,946 per worker. A third offense can cost $8,369 to $27,894 per worker. For a small business, a third offense with just five workers could mean penalties over $139,000.
Companies using E-Verify face another penalty. Failing to resolve a Final Nonconfirmation while continuing to employ the worker can lead to fines from $973 to $1,942 per employee.
These are real financial consequences. Our detailed breakdown of I-9 compliance penalties explains how these fines are calculated.
Criminal Penalties: When Violations Become a “Pattern or Practice”
While civil fines hurt your finances, criminal penalties can cost you your freedom.
Criminal penalties apply when violations show a pattern or practice of deliberate, repeated unlawful conduct. This means systematically ignoring the law, not just making accidental errors.
A conviction can lead to fines up to $3,000 per unauthorized worker and imprisonment for up to six months. These penalties can apply to individuals, not just the company. Other charges can include conspiracy, harboring unauthorized individuals, or document fraud.
Examples include routinely accepting fake documents, failing to complete Form I-9, or keeping two sets of books to hide cash payments to unauthorized workers. These actions show criminal intent.
The best defense is consistent, documented compliance. Regular internal audits show good faith efforts to follow the law. Our guide to the ICE I-9 audit process explains what auditors look for.
Beyond Fines: Document Abuse and Discrimination Penalties
I-9 audit penalties also include discrimination and document abuse charges, enforced by the Department of Justice’s Immigrant and Employee Rights Section (IER).
Document abuse often occurs when employers, trying to be careful, overstep. It includes requesting specific documents when an employee has already provided sufficient proof, or rejecting valid documents out of uncertainty. For example, asking only certain employees for a passport is discriminatory. These actions are considered discriminatory, regardless of intent. For 2025, document abuse violations cost between $230 and $2,304 per violation, as detailed in the Federal Register’s penalty adjustments.
Unfair immigration-related employment practices cover broader discrimination based on national origin or citizenship status. Penalties are tiered: $575 to $4,610 for a first offense, $4,610 to $11,524 for a second, and $6,913 to $23,048 for subsequent offenses.
The key to avoiding discrimination claims is consistency. If you photocopy documents for one employee, you must do it for all. The IER investigates these complaints thoroughly, and ignorance is not a defense.
How ICE Calculates I-9 Audit Penalties
Understanding how ICE calculates I-9 audit penalties is straightforward. The process involves a base fine calculation, adjustments for specific circumstances, and annual inflation increases.

After an audit, ICE calculates a base fine using a “violation percentage.” This is the number of violations divided by the total number of Forms I-9 audited, which sets the initial penalty range. But the base fine is just the starting point.
The NIF and the Five Factors That Determine Your Final Fine
When ICE finds violations, they issue a Notice of Intent to Fine (NIF) detailing the violations and proposed fine. You have 30 days to request a hearing with the Office of the Chief Administrative Hearing Officer (OCAHO). Additional information about OCAHO.
If you miss the deadline, the penalty becomes final and cannot be appealed. DHS will issue a Final Order, and the amount is set.
ICE then adjusts the base fine using five statutory factors. Each factor can increase or decrease your fine by up to 25%, significantly moving the needle on the final amount.
-
The size of your business is considered. Larger businesses often face higher penalties, but small companies are not exempt.
-
Your good faith effort to comply can help. Evidence of good faith, such as regular internal audits and prompt error correction, can reduce your fine. Resources like Auditing I-9 Forms can help demonstrate this commitment.
-
The seriousness of the violation has substantial weight. ICE weighs the nature of each violation, from a missing date to knowingly hiring an unauthorized worker.
-
The involvement of unauthorized workers dramatically increases the fine. This factor alone can push penalties to the maximum.
-
Your history of previous violations will lead to higher penalties. ICE is stricter with repeat offenders.
These five factors represent your opportunity to demonstrate compliance efforts and potentially reduce penalties.
The Impact of Annual Inflation Adjustments on Fines
A final piece of the I-9 audit penalties puzzle is inflation adjustments. The Federal Civil Penalties Inflation Adjustment Act requires DHS to adjust penalties annually. This is a non-discretionary, statutory requirement.
In 2024 alone, fines increased by approximately three percent. Since December 2021, I-9 fines have seen an overall increase of 18.57%. The most recent Form I-9 Fine Matrix was published in the Federal Register on January 2, 2025.
This means procrastination is expensive. A violation that cost $2,000 a few years ago could cost over $2,371 today, and it will be even higher next year. Proactive compliance is an investment that protects you from these escalating costs. You can stay current by checking the Federal Register for adjustments.
If you need a refresher on the basics, our guide What is an I-9? provides a solid foundation.
Your Proactive Defense: A Guide to Avoiding Penalties
The best way to handle I-9 audit penalties is to avoid them. A proactive approach, built on consistent practices, regular audits, and smart tools, can shield your business from violations.

Being prepared now saves you from future fines and legal headaches. Here are the practical steps to ensure compliance.
Best Practices for Conducting Internal I-9 Audits
Don’t wait for an ICE audit. Internal audits are your secret weapon, allowing you to find and fix mistakes before they become costly violations.
First, designate a specific, trained person to own I-9 compliance. This role requires authority and should be treated as substantive work, not just paperwork.
Schedule regular self-audits (annually, semi-annually, or quarterly). During these audits, examine a sample of forms. Check that you are using the correct form version (mandatory since November 1, 2023) to avoid easy penalties.
Check the timing on every form. Section 1 must be completed by the employee’s first day, and Section 2 must be finished within three business days of their start date. Late forms are a serious violation.
Look for completeness and accuracy. Blank spaces, missing signatures, and inconsistent information are all violations. Establish a clear correction process for errors. The original completer should initial and date any changes. Never use white-out.
Verify that you’re only accepting documents from the acceptable list and that they appear genuine. This is a common stumbling block that can lead to penalties.
Finally, follow retention requirements. Keep forms for three years from hire or one year after termination, whichever is longer. Store I-9s separately from personnel files for easy access during an audit and to protect privacy.
For more details, see ICE guidance on internal I-9 audits and our Internal I-9 Audit Complete Guide.
How to Avoid Costly I-9 Audit Penalties with E-Verify
The E-Verify system can be a game-changer for reducing your risk of I-9 audit penalties. The system electronically confirms work authorization by checking Form I-9 data against government databases, providing quick confirmation in most cases.
However, E-Verify is not a magic bullet. You must understand your responsibilities, especially when handling a Final Nonconfirmation (FNC). Continuing to employ someone after an FNC without notifying DHS can cost you between $973 and $1,942 per employee.
Employers in good standing with E-Verify can use special procedures for remote document verification, which is crucial for hybrid and remote work. You must qualify for and follow these alternative procedures exactly.
Using E-Verify or electronic I-9 software does not give you a free pass, because human oversight is still essential. A trained professional must review documents to ensure they are unexpired, genuine, and relate to the employee. Technology helps, but it does not replace knowledgeable judgment.
E-Verify employers must also make and keep copies of documents presented for List A of Form I-9.
Learn more about making E-Verify work for you with our resources on E-Verify Compliance and the Remote I-9 Verification Guide.
Key Takeaways to Minimize Your I-9 Audit Penalties Risk
Avoiding I-9 audit penalties comes down to a few fundamental principles for a strong compliance foundation.
-
Be Consistent: Apply your I-9 policies the same way for every employee to avoid discrimination charges.
-
Be Timely: Section 1 must be done by day one, and Section 2 within three business days. These deadlines are federal requirements.
-
Invest in Training: Anyone who touches the I-9 process needs comprehensive, regular training on the latest rules.
-
Conduct Self-Audits: Regular internal audits help you catch and fix problems proactively and demonstrate good faith.
-
Stay Informed: Monitor official sources like USCIS and the Federal Register for updates on rules, forms, and penalties.
-
Know When to Ask for Help: For complex situations, consult with experts to avoid expensive mistakes.
For a broader view, see our Employment Compliance Ultimate Guide.
Frequently Asked Questions about I-9 Compliance
Employers often have the same worries about Form I-9 rules and the risk of costly I-9 audit penalties. Here are answers to some of the most common questions.
What is the most common I-9 violation?
The most common I-9 violation is paperwork errors. These are not dramatic violations but simple, frustrating mistakes that can cost thousands per form.
Common errors include missing dates, incomplete sections, missing signatures, missed deadlines, and using outdated forms. These violations are entirely preventable with proper training and internal reviews. When they accumulate, fines add up quickly.
Can I be penalized if all my employees are authorized to work?
Yes, and this surprises many employers. Even if all your employees are authorized to work, you can still be penalized.
The government audits your verification process, not just your employees’ work status. Process compliance is mandatory. Paperwork violations carry fines regardless of your employees’ authorization status. Errors like missing signatures or late completion can result in penalties from $281 to $2,789 per form.
Does using electronic I-9 software make me immune to penalties?
No. While electronic I-9 software like our Electronic I-9 Solutions is an excellent tool for reducing errors and streamlining verification, it does not make you immune to penalties.
Human error is still a factor. Software cannot judge if a document is genuine or relates to the person presenting it. Trained professional oversight is critical for reviewing documents to ensure they are unexpired and appear authentic.
While software helps with form management and deadlines, key processes like document review and reverification still rely on human diligence. The bottom line is that electronic systems are powerful allies in avoiding I-9 audit penalties, but they must be combined with proper training and careful human oversight.
Secure Your Business from I-9 Risks
I-9 compliance can feel overwhelming with serious penalties and rising enforcement. With the right partner, however, you can make this challenge a manageable part of your business.
At Valley All States Employer Service, our mission is to help you avoid I-9 audit penalties and stay compliant. We handle the complex paperwork so you can focus on your core business.
We specialize in outsourced E-Verify workforce eligibility verification, taking the administrative burden off your shoulders. Our expert, impartial guidance acts as a safety net, minimizing errors before they become costly violations.
We tailor our services to businesses of all sizes, helping you implement best practices, conduct internal audits, and stay current with evolving regulations. I-9 compliance is increasingly complex, with climbing penalties and strict enforcement. The margin for error is small, but you don’t have to face it alone.
Our goal is to keep you compliant so you can focus on your business. We handle the details, the updates, and the verification processes, providing peace of mind that your I-9 process is done right.
Ready to master your I-9 compliance and avoid costly penalties? Explore our I-9 Audit Complete Guide for in-depth strategies and support. Let’s work together to protect your business from unnecessary risk.