Why Every HR Manager Needs to Master the I-9 Self Audit
An I-9 self audit is a proactive review of your company’s Form I-9 files to identify and correct errors before federal inspectors arrive at your door. Here’s what you need to know:
Key Steps for an I-9 Self Audit:
- Gather all I-9 forms for current and terminated employees
- Create an employee roster to match against existing forms
- Review each section of every form for completeness and accuracy
- Identify and log errors using a systematic checklist
- Correct mistakes with proper documentation and dating
- Organize findings with audit memos and retain records
- Implement ongoing processes to prevent future violations
With the new administration’s immigration enforcement efforts ramping up, many HR managers are casting worried glances at their I-9 files. And they should be.
Here’s the sobering reality: An estimated 60-80% of all completed Forms I-9 contain at least one error. Even simple clerical mistakes can result in fines ranging from $252 to $25,076 per violation. When ICE shows up with a Notice of Inspection, you typically have just 72 hours to produce all your I-9 documentation.
But here’s the good news. Conducting regular I-9 self audits demonstrates good faith compliance efforts. This documented commitment to following the rules can significantly reduce penalties if violations are found during a federal audit.
Smart HR managers don’t wait. They audit themselves first.

What You’ll Learn
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every aspect of conducting an effective I-9 self audit. We’ll cover the legal requirements, step-by-step procedures, common pitfalls to avoid, and best practices for maintaining ongoing compliance.
By the end of this article, you’ll understand how to:
- Identify the most common I-9 violations before they become costly penalties
- Implement a systematic audit process that demonstrates good faith compliance
- Correct errors properly without creating additional legal exposure
- Establish ongoing procedures to prevent future violations
Why an I-9 Self Audit Matters
ICE fines for I-9 violations start at $252 per violation and can skyrocket to $25,076 depending on how serious the mistakes are and your company’s compliance track record. Picture this: you have 100 employees, and even minor violations across all your forms could slam you with penalties exceeding $250,000.
When ICE shows up with a Notice of Inspection, you get exactly three business days to produce every piece of I-9 documentation they want to see. Companies that can’t deliver face work authorization raids, criminal sanctions, and in the worst cases, forced business shutdowns.
The enforcement landscape has completely changed. Immigration and Customs Enforcement has made headlines with surprise raids on companies over I-9 paperwork violations. No industry gets a free pass. Agriculture, manufacturing, construction, hospitality, and service industries have all felt the heat.
Here’s the part that really stings: you’re on the hook for every single I-9 form in your files. That includes forms completed by HR staff who left years ago, paperwork inherited when you acquired another company, and documents created by well-meaning employees who had no clue what they were doing.
The silver lining? Conducting regular I-9 self audits can serve as your best defense. ICE actually looks favorably on companies that demonstrate good faith efforts to stay compliant. When they see documented self-audits, proper correction procedures, and ongoing training, they often reduce penalties significantly when violations are found.
The Hidden Costs of Non-Compliance
Beyond those eye-watering fines, I-9 violations create hidden costs that can devastate your business operations.
Lost productivity hits you immediately. When ICE arrives for an inspection, your entire HR team drops everything to compile documentation. Normal operations grind to a halt.
Legal fees add up fast. Defending against I-9 violations requires specialized immigration attorneys. Even straightforward cases can generate thousands in legal costs.
Reputational damage spreads like wildfire. News of ICE raids and compliance violations travels quickly through local business communities, hurting customer relationships and employee morale.
Systemic mistakes multiply your pain. The most expensive violations happen when simple errors get repeated across multiple forms. A missing signature on every I-9 in your files transforms a $252 fine into tens of thousands in penalties.
Real Enforcement Numbers
ICE worksite enforcement has increased dramatically, with I-9 audits now representing the most common form of workplace immigration enforcement. The 72-hour deadline when ICE issues a Notice of Inspection catches many employers completely off guard.
Certain industries face heightened scrutiny. Agriculture, manufacturing, construction, hospitality, and food service companies report much higher audit rates. However, enforcement actions have expanded to include professional services, healthcare, and technology companies.
The Guidance for Employers Conducting Internal Audits provides official direction on how to structure compliant I-9 self audit procedures.
Legal Foundations & Retention Rules
The Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986 (IRCA) requires every employer to complete Form I-9 for every person hired after November 6, 1986, regardless of their citizenship status.
The timing requirements are non-negotiable. Section 1 must be completed by your new employee no later than their first day of work. Section 2 falls on you as the employer within exactly three business days from the employee’s start date. Section 3 comes into play when an employee’s work authorization expires or when you rehire someone within three years.
The document requirements follow a simple but strict system. List A documents like passports establish both identity and work authorization. List B documents such as driver’s licenses prove identity only, while List C documents like Social Security cards establish work authorization only. Your employees can present either one List A document or one document from both List B and List C.
Here’s a critical point: you cannot tell employees which documents to bring. This violates anti-discrimination laws. If a document appears genuine and relates to the person presenting it, you must accept it.
Retention rules require keeping I-9 forms for three years after the date of hire for current employees. For terminated employees, you need to retain forms for three years after the hire date OR one year after termination, whichever comes later.
| Employee Status | Retention Period |
|---|---|
| Current Employee | 3 years from hire date |
| Terminated Employee | 3 years from hire OR 1 year from termination (whichever is later) |
Remote hiring flexibilities that existed during the pandemic have expired, so you’re back to requiring physical document inspection for new hires.
Anti-discrimination provisions require equal treatment during the I-9 process. You cannot specify which acceptable documents an employee must present, nor can you reject documents that appear genuine and relate to the person presenting them.
California employers face an additional requirement to notify affected employees and collective bargaining representatives within 72 hours of receiving notice of a federal I-9 inspection.
For the most current guidance and forms, bookmark I-9 Central, USCIS’s official resource center.
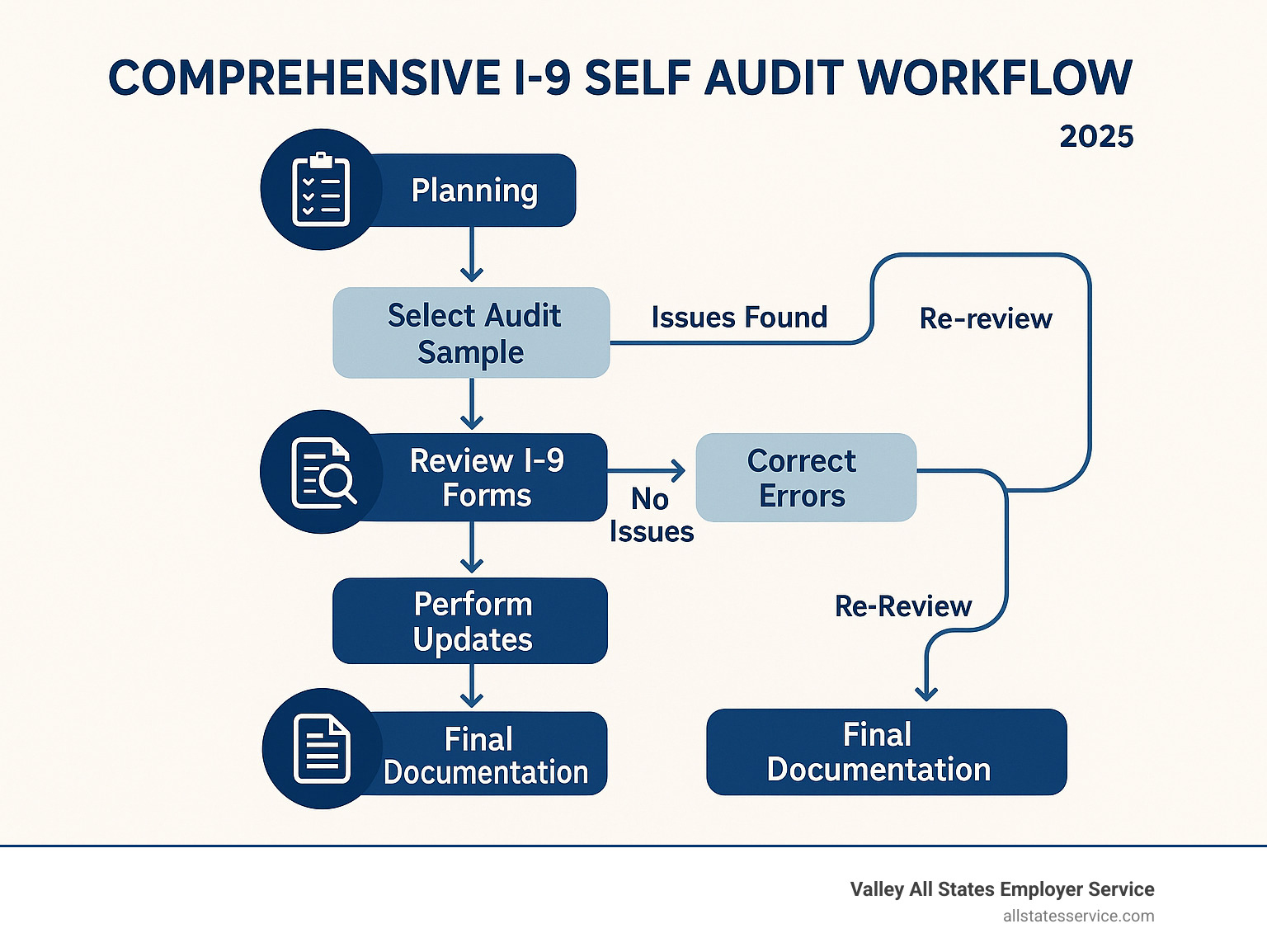
How to Conduct an I-9 Self Audit – Step by Step

The key to a successful I-9 self audit lies in systematic preparation and methodical execution. Whether you’re auditing 50 forms or 5,000, the process remains fundamentally the same.
Start by defining your audit scope. Smaller employers should review every I-9 form on file. Larger organizations may conduct sampling audits using neutral, non-discriminatory criteria.
Create a comprehensive employee roster including all workers hired after November 6, 1986. Cross-reference this roster against your I-9 files to identify missing forms.
Priority order for your audit:
- Current employees missing I-9 forms (immediate compliance risk)
- Current employees with incomplete or incorrect I-9 forms
- Terminated employees within the retention period
Establish an audit log to document every error found and corrective action taken. This log serves as evidence of your good faith compliance efforts.
For additional guidance on maintaining comprehensive HR compliance programs, explore our More info about Employer HR Compliance resources.
Plan Your I-9 Self Audit
Before diving into form review, establish a clear audit policy and procedure.
Timing matters. We recommend conducting I-9 self audits bi-annually during slower business periods when HR staff can dedicate focused attention to the process.
Assign a lead auditor with thorough knowledge of I-9 requirements. This person should complete refresher training before beginning the audit.
Consider attorney-client privilege. Some employers engage legal counsel to oversee their internal audits, potentially protecting audit communications under attorney-client privilege.
Gather essential resources before starting:
- Current Form I-9 with instructions
- USCIS Handbook for Employers (M-274)
- List of acceptable documents
- Audit checklist and log templates
Conduct the I-9 Self Audit
Begin with your employee roster and systematically work through each I-9 form using a standardized checklist.
Section 1 Review:
- Verify all personal information is complete and legible
- Confirm citizenship status is properly indicated
- Check for required signatures and dates
Section 2 Review:
- Verify document information matches acceptable documents lists
- Confirm document numbers and expiration dates are recorded
- Check that employer signature is present and dated within three business days of hire
Section 3 Review:
- Verify reverification is completed when required
- Check rehire information is properly documented
Common Errors to Identify:
- Missing signatures or dates
- Illegible handwriting
- Incomplete fields
- Wrong form version
- Invalid document combinations
- Expired documents accepted
Document & Preserve Findings
Proper documentation of your audit findings is essential for demonstrating good faith compliance efforts.
For error corrections:
- Draw a line through incorrect information (never use correction fluid)
- Enter correct information clearly
- Initial and date all corrections
- Attach explanatory memos when necessary
When to complete a new form:
- Multiple errors make the original form difficult to read
- Substantive errors require extensive corrections
Maintain comprehensive audit logs including:
- Employee name and identification
- Type of error found
- Corrective action taken
- Date of correction
- Auditor signature
Fixing Issues & Handling Red Flags

The moment you find problems during your I-9 self audit, your response can make or break your compliance efforts. Never attempt to hide mistakes or make corrections that could appear deceptive. ICE auditors have seen every trick in the book.
The correction process is straightforward but must be followed precisely. When employees need to fix Section 1 errors, they should draw a clean line through the incorrect information, write the correct details nearby, then initial and date the change. If the form looks messy after multiple corrections, have the employee complete a fresh Section 1.
For Section 2 and 3 errors, you or your authorized representative handles the corrections using the same line-through method. Every change gets your initials and the date.
Communication with employees requires a delicate touch. When you need to request corrections or additional documentation, avoid language that sounds like you’re targeting specific workers. Refer them to the acceptable documents list and let them choose what works best.
The official guidance on Self-Audits and Correcting Mistakes from USCIS provides detailed instructions for handling these situations correctly.
Missing or Incomplete I-9s
Missing forms for current employees represent your highest priority risk. Every person hired after November 6, 1986, must have a completed Form I-9 on file. When you find these gaps, complete the form immediately using current acceptable documents.
Use today’s date for completion, not the original hire date. Attach a memo explaining that you found the missing form during your audit and completed it as soon as possible.
For incomplete forms, identify exactly what’s missing. Have the right person fill in the blanks, date their completion, and document the correction in your audit log.
Suspect or Fake Documents
Finding potentially fraudulent documents creates one of the most challenging situations in I-9 compliance. Start with a careful second look. Have another authorized representative review them. Document your specific, objective concerns.
You can reject documents that are clearly expired, obviously altered, or don’t reasonably appear to relate to the person presenting them. You cannot reject documents because you’re unfamiliar with the format.
When addressing questionable documents with an employee, focus on observable issues. Keep the conversation about the document, not the person.
If you suspect a pattern of fraudulent documents across multiple employees, you may report this to ICE through their tip line at 1-866-DHS-2-ICE.
When to Call in a Third-Party Auditor
Consider professional help when your company is going through major changes like mergers and acquisitions or rapid growth that overwhelms your HR team’s ability to maintain proper procedures.
If your internal audit reveals significant violations that could trigger substantial penalties, professional auditors bring specialized expertise you might not have in-house.
For organizations needing comprehensive compliance support, our More info about E-Verify Services can help you understand how professional verification services complement your internal audit efforts.
Best Practices for Continuous Compliance

Think of I-9 self audit compliance like maintaining your car. You wouldn’t wait for your engine to seize before changing the oil, would you? Smart HR managers build compliance into their daily operations instead of scrambling when problems surface.
Bi-annual audit schedules create the perfect rhythm for staying ahead of issues. Schedule your major reviews during quieter business periods, typically late spring and early fall.
Your tickler system becomes your best friend for tracking critical dates. Modern HR software can automatically alert you when work authorization expires or reverification deadlines approach. Manual tickler files work fine for smaller operations.
Electronic storage systems offer game-changing advantages over traditional paper files. Digital I-9 management provides better security, easier organization during audits, and simplified search capabilities when ICE comes knocking.
Separate file organization prevents costly mistakes during retention periods. Keep distinct files for current employees and terminated employees whose I-9 forms you’re still required to retain.
Annual refresher training keeps your HR team sharp on I-9 requirements. Even experienced staff benefit from updates on new forms, policy changes, and common mistakes to avoid.
For organizations managing complex background check processes alongside I-9 compliance, our Pre-Employment Background Check Time resources help you coordinate these processes effectively.
Organize & Store I-9s Like a Pro
Digital systems offer superior organization, search capabilities, and security compared to paper files. Indexing systems should allow lightning-fast retrieval by employee name, hire date, or termination date.
Purge schedules ensure you retain forms for the required period without maintaining unnecessary files forever. Create calendar reminders for purge dates and document your disposal process.
Backup procedures protect against data loss or system failures that could leave you scrambling during an audit.
Keep Employees in the Loop
Individual notices work much better than group announcements for I-9 issues. Personalized communication reduces anxiety and prevents unnecessary questions from employees whose forms are perfectly compliant.
Clear deadlines help employees understand the urgency of compliance requirements. Provide specific dates for document submission and explain the consequences of missing deadlines.
Anti-retaliation reminders protect both employees and employers. Make it clear that employees won’t face negative consequences for raising questions about I-9 processes.
Frequently Asked Questions about I-9 Self Audits
How often should we perform an I-9 self audit?
The sweet spot for most organizations is twice a year. This bi-annual schedule gives you enough time to catch problems before they multiply while showing federal auditors that you’re serious about compliance.
Small businesses with stable workforces can often get away with annual audits. Larger organizations or those with high turnover should audit more frequently, sometimes quarterly.
Consider bumping up your audit schedule when you’ve had significant HR staff changes, completed mergers or acquisitions, or noticed increased enforcement activity in your industry.
What’s the difference between technical and substantive errors?
Technical errors are the paperwork equivalent of typos. Missing signatures, illegible handwriting, incomplete employer information, or minor transcription mistakes all fall into this category. You can fix technical errors right on the original form using the line-through method.
Substantive errors are the big ones that affect whether your I-9 is legally valid. Wrong citizenship status, invalid document combinations, accepting expired documents, or discriminatory document requirements all qualify as substantive errors. These problems typically require completing a new I-9 form entirely.
How long must we retain corrected forms and audit logs?
Your corrected I-9 forms follow the same retention rules as pristine originals: three years after hire date or one year after termination, whichever comes later.
Audit logs and supporting documentation should stick around for the same period as the I-9 forms they reference. This paperwork trail proves you’re making good faith efforts to stay compliant and can significantly reduce penalties during federal inspections.
Conclusion & Next Steps
Conducting regular I-9 self audits doesn’t have to be the dreaded task that keeps HR managers awake at night. When you approach it systematically, it becomes a powerful tool that protects your business while demonstrating your commitment to doing things right.
Think of it this way: would you rather find a problem during your own quiet review or when federal agents are standing in your lobby with a 72-hour deadline? The choice seems pretty obvious when you put it like that.
The evidence is clear. Organizations that accept proactive I-9 self auditing consistently fare better during federal inspections. They pay lower penalties, resolve issues faster, and maintain better relationships with their workforce. More importantly, they sleep better at night knowing their compliance house is in order.
Here’s what successful companies do differently: they schedule their first comprehensive audit within 30 days of recognizing the need. They don’t wait for the perfect moment or the ideal software system. They start with what they have and improve as they go.
Your roadmap moving forward should include establishing those bi-annual audit cycles we discussed. Mark your calendar now for spring and fall reviews. Create simple tickler systems to track work authorization expirations. Train your team on proper correction procedures before they need to use them.
But let’s be honest about something. Not every organization has the internal bandwidth or expertise to handle complex I-9 compliance challenges. That’s where professional support makes the difference between stress and success.
At Valley All States Employer Service, we’ve seen how the right verification support transforms compliance from a burden into a competitive advantage. Our expert E-Verify processing services eliminate the guesswork and administrative headaches that trip up so many employers.
We understand the reality of modern HR departments. You’re juggling multiple priorities with limited resources. Our impartial, efficient E-Verify processing lets you focus on strategic initiatives while we handle the compliance details that keep you protected.
Whether you need comprehensive support through our I-9 Verification Assistance services or you’re ready to streamline your entire verification process, we’re here to help you succeed.
The difference between reactive and proactive compliance often comes down to having the right partner. Don’t wait for that ICE notice to arrive. Take control of your I-9 compliance today, and find how much easier employment verification can be when you have expert support.
Ready to transform your approach to I-9 self audits and create bulletproof compliance procedures? Contact us today to learn how our professional verification services can give you the confidence that comes with knowing you’re doing everything right.