E-Verify verification system: Essential 2025 Guide
Why the E-Verify Verification System is Critical for Modern Businesses
The E-Verify verification system is a web-based tool that allows employers to confirm whether their newly hired employees are authorized to work in the United States. This government-operated system compares information from Form I-9 against records from the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) and Social Security Administration (SSA) to verify employment eligibility.
Key Facts About E-Verify:
- Purpose: Confirms employee work authorization electronically
- Speed: Results provided in 3-5 seconds
- Cost: Free government service
- Coverage: Available in all 50 states and U.S. territories
- Users: Nearly 1 million companies enrolled as of recent data
- Accuracy: 98.88% of applicants approved to work as of 2018
For busy HR managers juggling complex compliance requirements, understanding E-Verify isn’t optional anymore. Federal contractors must use it. Many states now mandate it for certain employers. Even when voluntary, E-Verify offers the “best means available” to electronically confirm employment eligibility.
But here’s the challenge: while E-Verify seems straightforward, the reality involves navigating case results, handling Tentative Nonconfirmations, understanding employee rights, and maintaining strict compliance timelines. A single misstep can lead to penalties or discrimination claims.
The stakes are high. With over 48 million E-Verify cases processed and strict federal oversight, employers need more than basic knowledge. They need a clear roadmap for implementation and ongoing compliance.
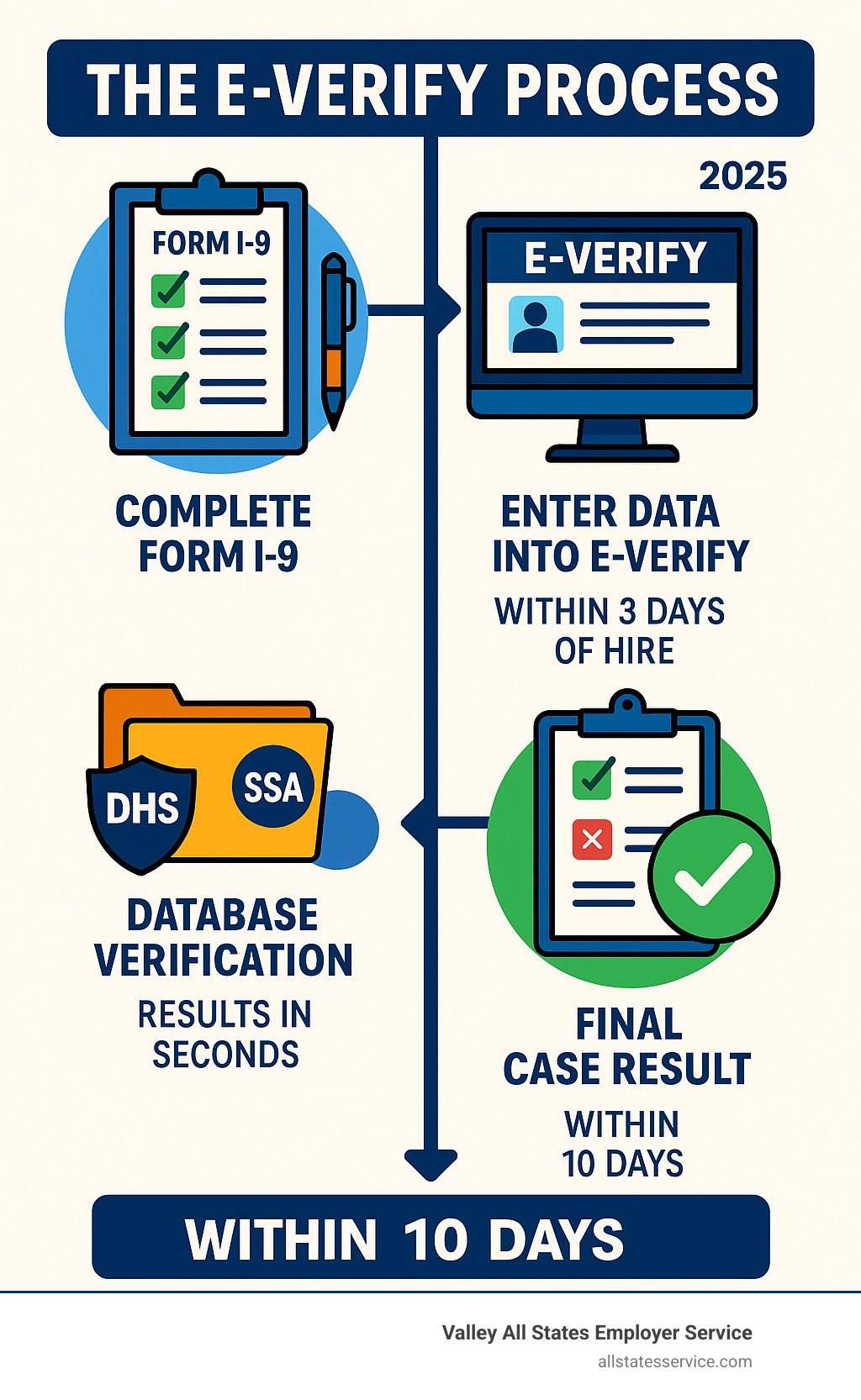
What is E-Verify and How Does It Work?
Think of the E-Verify verification system as your digital employment detective. This web-based platform, run by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) working hand-in-hand with the Social Security Administration (SSA), helps you confirm that your new hires are legally authorized to work in the United States.
Unlike the paperwork-heavy processes of the past, E-Verify brings employment verification into the digital age. It’s fast, it’s free, and when used correctly, it gives you confidence that you’re building a legally compliant workforce.
The Core Process: From Form I-9 to Verification
Every E-Verify case starts with something you’re already familiar with: Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification. This form has been the foundation of employment verification since 1986, and it’s not going anywhere. Every single new employee must complete their I-9, showing you documents that prove both their identity and work authorization.
Here’s where the E-Verify verification system steps in to make your life easier. You take specific information from that completed Form I-9 and enter it into E-Verify’s online portal. The system creates a case for that employee and gets to work immediately.
The speed is honestly impressive. Most cases get resolved in three to five seconds. That’s faster than it takes to make a cup of coffee. This quick turnaround means you can verify employees and get them started without lengthy delays.
E-Verify doesn’t replace Form I-9. Think of it more like a digital assistant that double-checks the I-9 information against government records. They work together, but they have different rules and requirements. For a deeper dive into how these two systems complement each other, check out our guide on E-Verify and I-9.
The system follows what’s called the three-day rule. You must create an E-Verify case no later than three business days after your employee starts work. Miss this deadline, and you could face compliance issues.
The Role of Government Databases: DHS and SSA
The real power behind E-Verify lies in its connection to massive government databases. When you submit a case, the system instantly compares your employee’s information against records held by both the Social Security Administration and the Department of Homeland Security.
The SSA records primarily verify that the employee’s name matches their Social Security number in government files. It’s like having a direct line to the Social Security Administration to confirm the basics are correct.
The DHS records handle the immigration side of things. This database checks work authorization documents, immigration status, and other identity information for non-citizens. It’s particularly important for employees who presented documents like Employment Authorization Documents or Permanent Resident Cards.
When everything matches up perfectly, you’ll get an “Employment Authorized” result. This means the employee’s information aligns with what the government has on file, and you can proceed with confidence.
The accuracy rates are impressive, with the system correctly processing the vast majority of cases. However, no system is perfect, which is why understanding the full verification process is crucial. The data security measures are robust, protecting sensitive employee information throughout the verification process.
Want to learn more about the broader employment verification landscape? Our E-Verify Employment Verification page covers additional insights that can help streamline your hiring process.
The E-Verify Verification System: Who Must Use It and Why?
Here’s where things get interesting: while the E-Verify verification system is available nationwide, it’s not a one-size-fits-all requirement. Think of it as a complex web of federal rules, state laws, and business choices that determine who must use E-Verify and who simply chooses to.
The system operates across all 50 states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, Guam, the U.S. Virgin Islands, and the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands. But just because it’s available everywhere doesn’t mean everyone has to use it. Understanding when E-Verify becomes mandatory versus optional can save you from compliance headaches down the road. For a comprehensive look at these requirements, check out our guide on E-Verify Employer Requirements.
Federal Mandates: Contractors and Beyond
The federal government takes E-Verify seriously, especially when taxpayer money is involved. If you’re a federal contractor or subcontractor, the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) likely requires you to use the E-Verify verification system. This isn’t just a suggestion, it’s the law.
Here’s what makes this requirement particularly important: it often applies to all employees assigned to the federal contract, not just new hires. That means if you land a federal contract, you might need to verify workers who’ve been with you for years. It’s the government’s way of ensuring that federal dollars support a legal workforce from top to bottom.
The rules extend beyond prime contractors too. Subcontractors working on federal projects often find themselves subject to the same E-Verify requirements. This creates a ripple effect throughout the federal supply chain. Our Federal E-Verify Rules page breaks down these complex requirements in detail, and for contractors specifically, we have a dedicated resource on E-Verify for Contractors.
A Patchwork of State Laws
If federal requirements weren’t complex enough, individual states have created their own E-Verify rules. The result? A true patchwork of requirements that varies dramatically depending on where you do business.
As of recent counts, 22 states require E-Verify for some or all employers. But here’s where it gets tricky: these laws are far from uniform. Some states mandate E-Verify for all employers, while others focus only on public employers or state contractors. Certain states tie E-Verify use to business licensing, making it a condition of operating legally. Others base requirements on company size, exempting smaller businesses from the mandate.
Take Arizona and Mississippi, for example. These states have been pioneers in requiring E-Verify for private businesses. Meanwhile, California took the opposite approach, actually prohibiting municipalities from mandating E-Verify use. This diverse legal landscape means you can’t assume what works in one state will apply in another.
The complexity is real, and it’s why employers often feel overwhelmed trying to steer state-specific requirements. As one comprehensive analysis notes in “An Overview of E-Verify Policies at the State Level,” the variation between states creates significant compliance challenges for multi-state employers.
Voluntary Participation: Why Some Employers Choose E-Verify
Even when the law doesn’t require it, many smart employers choose to enroll in the E-Verify verification system. Why voluntarily add another step to your hiring process? The benefits often outweigh the administrative burden.
Good-faith compliance is perhaps the strongest motivator. E-Verify provides what many consider the best available electronic method to confirm work authorization. This helps employers avoid the serious legal and financial risks that come with knowingly hiring unauthorized workers.
There’s also the corporate responsibility angle. Using E-Verify sends a clear message that your company is committed to maintaining a legal workforce and following ethical hiring practices. In today’s business environment, this kind of commitment can be valuable for your reputation and stakeholder relationships.
Perhaps most importantly, E-Verify offers peace of mind. When the system returns an “Employment Authorized” result, you have strong assurance that your employee is eligible to work. This certainty can be incredibly valuable, especially for businesses operating in industries with high compliance scrutiny.
Small businesses, in particular, often find that voluntary E-Verify participation helps level the playing field with larger competitors who may be required to use the system. Our E-Verify for Small Businesses guide explores how smaller employers can benefit from this choice.
The bottom line? Whether E-Verify is mandatory or voluntary for your business, understanding the system and its requirements is crucial for staying compliant and protecting your company.
Navigating E-Verify: Case Results, Timelines, and Employee Rights

Think of the E-Verify verification system like a conversation between computers. You submit information, and the system responds with one of several possible answers. Understanding these responses and knowing exactly what to do next can make the difference between smooth sailing and compliance headaches.
Here’s the reality: most of the time, E-Verify works seamlessly. But when it doesn’t, both employers and employees need to know their rights and responsibilities. The good news? With the right knowledge, even complex situations become manageable. If you need support navigating these waters, our E-Verify Customer Support team has your back.
Understanding E-Verify Case Results
When E-Verify processes your case, it returns one of six possible results. Each one tells a different story about what happens next.
Employment Authorized is the result everyone hopes for. It means the employee’s information matched government records perfectly, confirming they’re authorized to work in the U.S. This happens in the vast majority of cases. As of 2018, a remarkable 98.88% of E-Verify applicants received this green light, often within just seconds of submission.
E-Verify Needs More Time simply means the system requires additional processing. Your case gets automatically forwarded to DHS for further review. No action needed from you or your employee at this stage.
Tentative Nonconfirmation (TNC) is where things get more interesting. This doesn’t mean your employee can’t work. It means E-Verify found a mismatch between what you entered and what’s in government records. Out of over 48 million cases processed through May 2023, only 738,507 resulted in mismatches. That’s roughly 1.5% of all cases.
Case in Continuance appears when an employee is actively working to resolve a TNC. Think of it as the “work in progress” status.
Close Case and Resubmit typically means someone made a data entry error. The solution? Double-check your information, correct any mistakes, and try again.
Final Nonconfirmation (FNC) is the rarest result. It occurs when an employee either chooses not to contest a TNC or contests it but can’t resolve the mismatch. This confirms the employee isn’t authorized to work. Remarkably, only 0.011% of all cases end up as contested but unresolved mismatches.
Handling a Tentative Nonconfirmation (TNC)
Getting a TNC can feel alarming, but most TNCs get resolved successfully. The key is following the process correctly and respecting employee rights every step of the way.
Your first responsibility is notifying the employee privately about the TNC result. You must provide them with a “Referral Date Confirmation” notice. Privacy matters here. Don’t discuss this in front of other employees or make it a public matter.
The employee then has eight federal government workdays from the referral date to begin resolving the mismatch with the appropriate agency. This isn’t eight calendar days, it’s eight business days when federal offices are open. They’ll need to contact either the SSA for Social Security issues or DHS for immigration-related discrepancies.
Here’s the critical part: no adverse action allowed. You cannot fire, suspend, or change the employee’s working conditions based solely on a TNC. The employee must continue working normally while they resolve the issue. This protection is fundamental to the process and violating it can lead to discrimination claims.
The resolution process varies depending on the type of mismatch. Sometimes it’s as simple as updating a name change with Social Security. Other times, it might involve more complex immigration documentation issues. The employee can find detailed guidance in the USCIS Employee Rights Toolkit.
If the employee successfully resolves the TNC, their case status updates to “Employment Authorized.” If they choose not to contest or can’t resolve the mismatch, the case results in a Final Nonconfirmation. At that point, you have clear guidance on employment eligibility.
E-Verify’s overall accuracy rate for employment-authorized workers was approximately 94% as of 2012. The system continues to improve, but understanding how to handle the exceptions ensures you stay compliant while treating employees fairly.
E-Verify’s Broader Impact and Considerations
The E-Verify verification system touches millions of workers and employers every year, creating ripple effects that extend far beyond simple compliance checking. When you’re considering whether to use E-Verify or trying to understand its place in your business, it helps to see the bigger picture.
Think about it this way: with nearly 48 million cases processed, E-Verify has quietly become one of the most influential employment tools in America. But like any powerful system, it comes with both benefits and challenges that deserve honest discussion.
Benefits and Drawbacks for Employers
Let’s start with the good news. E-Verify offers some genuinely impressive advantages that make many employers enthusiastic users.
Speed and certainty top the list. Getting work authorization confirmation in 3-5 seconds feels almost magical compared to the old days of wondering if your paperwork was complete. The system is also completely free to use, which removes cost barriers for businesses of all sizes.
Perhaps most importantly, E-Verify provides significant risk reduction. When you get that “Employment Authorized” result, you have strong evidence of good-faith compliance. This protection becomes invaluable if you ever face an audit or investigation. Smart businesses recognize that avoiding penalties and legal headaches makes the administrative effort worthwhile. Understanding your E-Verify Compliance Cost means looking at both direct expenses and avoided risks.
But let’s be realistic about the challenges. The administrative burden is real, even if the system is free. Someone needs to enter data, manage cases, and handle any complications that arise. Data entry errors happen, and they can create unnecessary TNCs that frustrate both employers and employees.
Here’s something that surprises many employers: E-Verify only confirms work authorization. It won’t tell you if someone has a criminal record or verify their education. If you need comprehensive screening, you’ll want to explore additional E-Verify Background Checks options.
Implications for International Students and Workers
For international students and workers, E-Verify can literally make or break employment opportunities. The rules vary dramatically depending on your work authorization type.
Students on CPT or standard OPT have more flexibility. Most employers can hire them without being enrolled in E-Verify. But here’s where it gets tricky: if you’re an F-1 student seeking a STEM OPT extension, your employer absolutely must be enrolled in the E-Verify verification system. No exceptions, no workarounds.
This requirement has created an interesting dynamic in the job market. STEM students often find themselves using the E-Verify search tool to identify potential employers before even applying for jobs. It’s an extra step that adds complexity to an already challenging job search.
For H-1B workers, the situation is different. Companies don’t need E-Verify enrollment to file H-1B petitions. However, if they’re federal contractors or operate in states with E-Verify mandates, they might end up using the system anyway.
Research shows that E-Verify’s impact on labor markets varies significantly by worker population. Studies suggest it reduces opportunities for unauthorized workers while potentially improving outcomes for legal immigrants and certain U.S.-born workers. You can find detailed Research on E-Verify’s labor market impact that explores these complex relationships.
Privacy Concerns and Criticisms of the E-Verify verification system
Despite its widespread adoption, the E-Verify verification system faces ongoing criticism from privacy advocates and civil liberties groups.
Data privacy concerns top the list. The system processes millions of records containing sensitive personal information. Critics worry about potential data breaches, government overreach, and the creation of a massive surveillance database. The American Civil Liberties Union and similar organizations argue that E-Verify edges us closer to a national ID system.
Accuracy issues also generate controversy. While the system boasts impressive accuracy rates, even small error percentages affect thousands of authorized workers. False positives can derail job opportunities and create significant stress for workers who must steer government bureaucracy to resolve mismatches.
The potential for discriminatory use adds another layer of concern. Some employers might be tempted to pre-screen applicants or selectively verify only certain workers, practices that violate E-Verify rules and federal anti-discrimination laws.
Identity theft risks present ongoing challenges. The system’s reliance on Social Security numbers and other sensitive data creates attractive targets for criminals. While security measures exist, the sheer volume of data processed makes the system a high-value target.
These criticisms highlight the ongoing tension between immigration enforcement goals and individual privacy rights. As E-Verify continues evolving, expect these debates to persist and influence future policy decisions.
Simplifying Compliance: E-Verify and Your Business

Running a business means juggling countless responsibilities, and employment compliance shouldn’t keep you up at night. The E-Verify verification system offers powerful tools to streamline your hiring process, but success depends on understanding how it fits into your overall compliance strategy. Think of it as adding a new piece to your HR toolkit rather than replacing everything you already do.
Smart employers know that effective compliance starts with solid E-Verify Best Practices. These aren’t just bureaucratic checkboxes. They’re practical steps that protect your business while making your life easier.
Key Differences Between Form I-9 and the E-Verify verification system
Here’s where things get interesting. Many employers assume E-Verify simply replaces Form I-9, but that’s not quite right. Form I-9 remains the foundation, while E-Verify adds an electronic verification layer on top.
Mandatory vs. Optional: Every single employer in the United States must complete Form I-9 for every new hire. No exceptions. The E-Verify verification system, however, is only mandatory for federal contractors and employers in states that require it. For everyone else, it’s a choice.
Document Requirements: Both systems accept documents from the familiar Lists A, B, and C. But here’s a crucial difference: if your employee presents a List B identity document for E-Verify, it must contain a photograph. Form I-9 doesn’t have this photo requirement for List B documents.
Reverification: When an employee’s work authorization expires, you can use Form I-9 to reverify their eligibility. E-Verify, however, cannot be used for reverification. This trips up many employers who assume the systems work identically.
Remote Examination: This is where things have gotten more flexible. Traditionally, Form I-9 required you to physically examine documents in person. Since August 1, 2023, employers enrolled in E-Verify can use alternative procedures for remote document examination, provided they follow specific steps.
These differences matter more than you might think. Mixing up the rules can lead to compliance headaches that nobody wants to deal with.
Getting Help and Staying Compliant
Nobody expects you to become an E-Verify expert overnight. The good news is that plenty of resources exist to help you steer the system successfully.
The official E-Verify website at E-Verify.gov serves as your primary resource hub. You’ll find comprehensive guides, user manuals, and the latest updates there. When you need direct help, the E-Verify Contact Center stands ready at 888-464-4218 or 877-875-6028 for TTY users. Employees with questions can call 888-897-7781.
Free webinars hosted by DHS cover everything from basic overviews to specific topics like handling Tentative Nonconfirmations. These sessions often answer questions you didn’t even know you had.
For many businesses, especially those with high turnover or limited HR resources, working with an employer agent makes perfect sense. These third-party services specialize in managing the entire E-Verify process. They review I-9 forms for technical errors, ensure timely submissions, and handle the administrative details that can overwhelm busy employers.
Valley All States Employer Service, for example, provides this exact type of E-Verify Employer Agent Service. Rather than adding another task to your already full plate, you can focus on running your business while experts handle your compliance needs.
The E-Verify verification system doesn’t have to be complicated. With the right approach and proper support, it becomes just another smooth part of your hiring process. The key is knowing when to handle things yourself and when to bring in the professionals.
Conclusion
The E-Verify verification system has become a cornerstone of employment compliance in today’s business world. Whether you’re a federal contractor who must use it or a business owner choosing to implement it voluntarily, understanding E-Verify isn’t just helpful anymore. It’s essential.
Throughout this guide, we’ve walked through the entire E-Verify journey. From how it builds on the familiar Form I-9 foundation to its lightning-fast database checks with DHS and SSA records. We’ve explored who needs to use it (and why some employers choose it even when they don’t have to), steerd the sometimes tricky world of case results and TNCs, and examined its broader impact on everything from labor markets to international students seeking work.
Here’s the reality: compliance complexity is only increasing. The stakes keep getting higher. A simple data entry mistake can trigger a TNC. Missing a deadline can lead to penalties. Handling employee rights incorrectly during the TNC process can result in discrimination claims. Each E-Verify case you process represents both an opportunity to verify work eligibility and a potential compliance risk.
The good news? You don’t have to steer this alone.
Risk mitigation starts with recognizing that the importance of accuracy in E-Verify extends far beyond just getting a green “Employment Authorized” result. It’s about protecting your business, your employees, and your reputation. It’s about having systems in place that work consistently, every single time.
This is where the outsourcing benefits become clear. At Valley All States Employer Service, we’ve built our entire business around one simple idea: employment verification should be accurate, efficient, and stress-free for employers. Our expert team handles the complexities so you can focus on what matters most to your business.
We understand that every case matters. Every deadline counts. Every employee deserves fair treatment throughout the process. Our expert, impartial, and efficient E-Verify processing means fewer errors, less administrative burden, and greater peace of mind for your HR team.
Ready to take the complexity out of employment verification? Streamline your hiring with expert employment verification services and find how much easier compliance can be when you have the right partner by your side.