Employment Eligibility Verification: Crucial 2025 Guide
Why Employment Eligibility Verification Is Critical for Every Employer
Employment eligibility verification is a federal requirement that every U.S. employer must follow when hiring new employees. The process confirms that workers are legally authorized to work in the United States and helps prevent unauthorized employment.
Key Components of Employment Eligibility Verification:
- Form I-9 – Required for every employee to verify identity and work authorization
- E-Verify – Electronic system that confirms I-9 information against government databases
- Document examination – Physical or remote review of acceptable identification documents
- Record retention – Storing completed forms for 3 years after hire or 1 year after termination
- Compliance deadlines – Employees complete Section 1 by first day, employers complete Section 2 within 3 business days
Federal law requires that every employer who recruits, refers for a fee, or hires an individual for employment in the U.S. must complete Form I-9, Employment Eligibility Verification. This isn’t optional – it applies to all employers, regardless of size, and covers both citizens and non-citizens.
The verification process has evolved significantly, especially since COVID-19. New options include remote document examination for qualifying E-Verify employers and a streamlined one-page Form I-9 that works on mobile devices. These changes aim to reduce administrative burden while maintaining security.
Non-compliance carries serious consequences. Employers face potential fines, penalties, and legal liability for failing to properly complete Form I-9 or participate in required E-Verify programs. With unemployment below 4% for 18 months and record numbers of new businesses starting, getting this process right from the start is more important than ever.
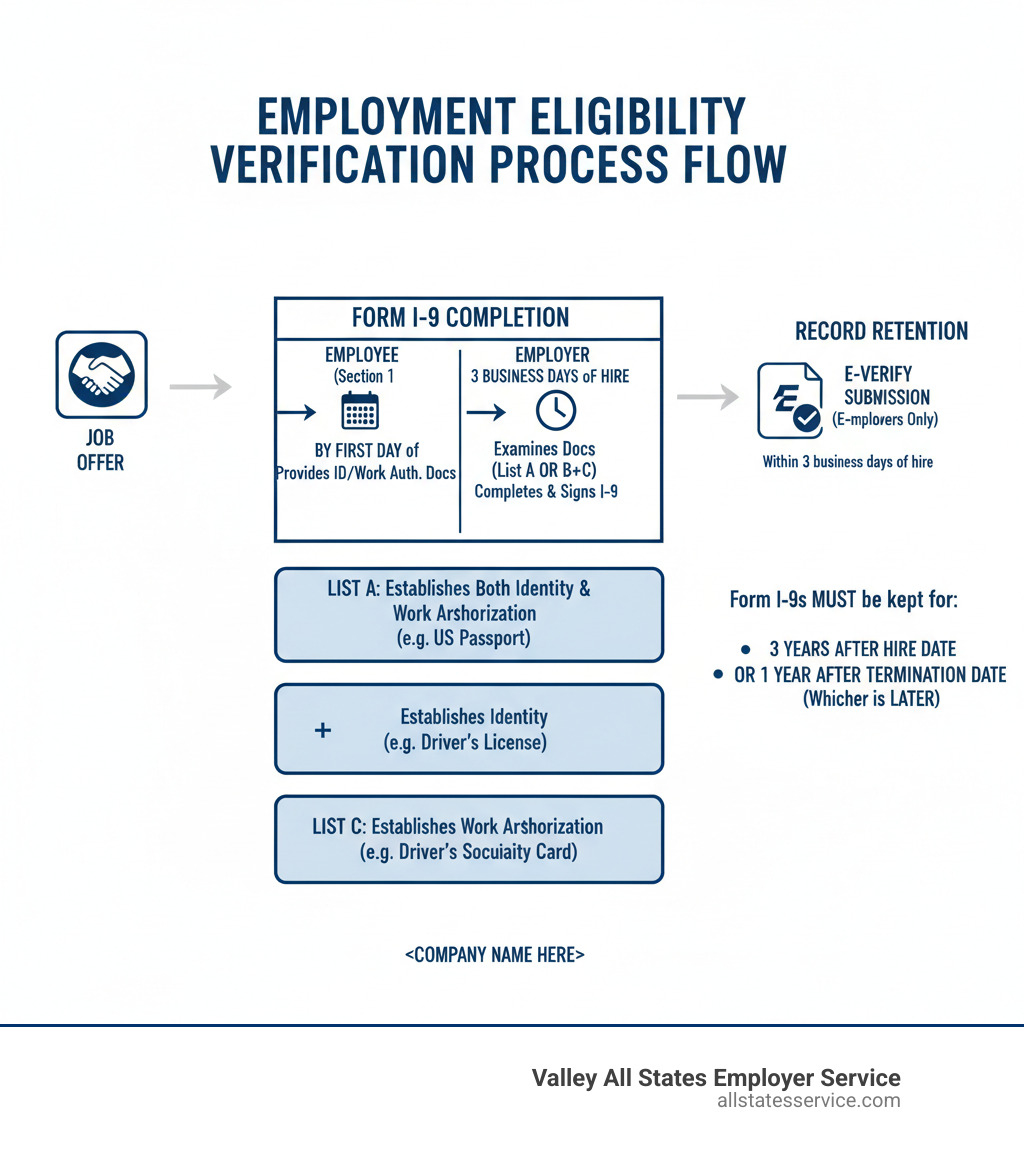
The Foundation: Understanding Form I-9
Think of Form I-9 as your business’s first line of defense against unauthorized employment. This single document, managed by U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS), has one clear mission: verifying the identity and employment authorization of every person you hire in the United States.
Whether you’re hiring your first employee or your hundredth, Form I-9 is non-negotiable. Every individual you bring onto your team, from citizens to non-citizens, must complete this process. It’s not just good practice, it’s federal law. For a complete breakdown of this essential document, check out our comprehensive guide on What is an I-9 Form?.
Here’s some good news: USCIS recently rolled out a streamlined, one-page version of Form I-9. Gone are the days of flipping through multiple pages. This updated form is mobile-friendly, offers clearer instructions, and provides better guidance on acceptable receipts and document extensions. It’s designed to make employment eligibility verification less of a headache for everyone involved.

The Employee’s Role in Employment Eligibility Verification
Your new employees have a straightforward but critical job: complete Section 1 of Form I-9 by their first day of work. No exceptions, no delays.
In Section 1, employees provide their personal information like name, address, date of birth, and Social Security number. The most important part? They must attest to their citizenship or immigration status by checking the appropriate box. This isn’t just paperwork, it’s their legal declaration that they have the right to work in the U.S.
Next comes document presentation. Here’s where employee rights really matter. Your new hire gets to choose which documents to present from the Lists of Acceptable Documents. You cannot demand specific documents or tell them what to bring. That choice belongs entirely to them. If you need help navigating these employee rights and ensuring fair treatment, our HR Compliance Assistance can guide you through the process.
The Employer’s Role in Employment Eligibility Verification
As an employer, you have three business days after an employee’s first day to complete Section 2 of Form I-9. This is where the document examination happens, and it requires careful attention to detail.
Your job is to review the documents your employee presented and ensure they reasonably appear genuine and relate to that person. You’ll record the document information on the form, but remember the golden rule: no discrimination. You cannot refuse valid documents, ask for additional paperwork beyond what’s required, or treat employees differently based on their citizenship status or national origin.
Sometimes you might use an authorized representative to handle Section 2 completion. This could be a notary, an HR professional, or a compliance service like Valley All States Employer Service. This approach works especially well for remote hires or when you need expert guidance to avoid costly mistakes.
The three-day rule is firm, but it’s three business days, not calendar days. Miss this deadline, and you’re looking at potential penalties and compliance issues. For detailed guidance on managing these responsibilities without the stress, explore our I-9 E-Verify Compliance Guide.
Completing the Form I-9: A Step-by-Step Process
Getting through the Form I-9 for employment eligibility verification doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. Think of it like following a recipe – you just need the right ingredients (documents) and proper timing to get it right every time.
The beauty of the new one-page Form I-9 is that it’s actually designed with real people in mind. Gone are the days of wrestling with multiple pages on your phone or tablet. This mobile-friendly version means you can complete the form anywhere, anytime, without the usual headaches.
The key to success? Understanding your deadlines and knowing which documents work. Let’s walk through exactly what you need to know.
What Documents Are Acceptable?
Here’s where many people get confused, but it’s actually pretty straightforward once you understand the system. The government has organized acceptable documents into three lists, and employees get to choose which ones they want to present. That’s right – you decide, not your employer.
You can either present one document from List A (which proves both who you are and that you’re authorized to work), or you can mix and match with one document from List B (proving identity) plus one document from List C (proving work authorization).
Here are some common examples from each list:
- List A (Establishes both identity and employment authorization): These documents do double duty. Common choices include a U.S. Passport, a Permanent Resident Card (or “Green Card”), or an Employment Authorization Document (EAD).
- List B (Establishes identity): These documents prove you are who you say you are. Most people use a driver’s license or a state ID card. Other options include a school ID with a photograph, a U.S. military card, or a voter’s registration card.
- List C (Establishes employment authorization): These documents show you are authorized to work. The most common is an unrestricted Social Security card. A certified copy of a birth certificate or a Certificate of Naturalization also works.
Whatever you choose must be unexpired. That expired driver’s license sitting in your wallet won’t cut it. For the complete official list with all the details, check out the Lists of Acceptable Documents from USCIS.

Deadlines and Timelines You Can’t Miss
When it comes to employment eligibility verification, timing isn’t just important – it’s everything. Miss these deadlines, and you’re looking at potential compliance issues that nobody wants to deal with.
For employees, Section 1 must be completed no later than your first day of work. But here’s the catch – you can’t fill it out before you’ve actually accepted the job offer. It’s like a perfectly timed dance move.
For employers, the clock starts ticking once your new hire walks through the door. You have exactly three business days after their first day to complete Section 2. If someone starts on Monday, you’ve got until Thursday. No exceptions, no extensions.
But wait, there’s more to consider. Reverification comes into play when an employee’s work authorization has an expiration date. Before that date arrives, you’ll need to complete the reverification process using Supplement B of Form I-9.
Rehires get special treatment. If someone returns within three years of their original Form I-9, you might be able to update their existing form instead of starting fresh. It’s a nice time-saver when done correctly.
The three-business-day rule is your best friend and your biggest challenge rolled into one. Plan ahead, especially for remote employees or when holidays might affect your timeline.
Don’t forget about record retention either. Those completed forms need to stick around for three years after hire or one year after termination, whichever comes later. It’s not just good practice – it’s required by law. For expert guidance on managing these records properly, our I-9 Record Keeping resource has you covered.
E-Verify and the Future of Employment Eligibility Verification
Think of E-Verify as your digital assistant for employment eligibility verification. This internet-based system, operated by the Department of Homeland Security (DHS) in partnership with the Social Security Administration (SSA), takes the guesswork out of confirming whether your new employees are authorized to work in the United States. The best part? It’s completely free and delivers results in just three to five seconds!
While most employers can choose whether to use E-Verify, it’s not optional for everyone. Federal contractors with contracts containing the Federal Acquisition Regulation (FAR) E-Verify clause must participate. Additionally, many states and local jurisdictions have jumped on board, requiring public agencies, government contractors, and sometimes even private employers to use the system.
Here’s what’s important to remember: E-Verify doesn’t replace Form I-9. Instead, it works alongside it to create a more robust verification process. If you’re wondering whether your business needs to participate, check out our detailed guide on What is E-Verify? and explore the specific E-Verify Employer Requirements that might apply to your situation.
How E-Verify Works with Form I-9
The beauty of E-Verify lies in its simplicity. Once you’ve completed the traditional Form I-9 process with your employee, E-Verify takes that same information and electronically compares it against millions of government records. It’s like having a direct line to verify what you’ve already documented.
Here’s how the process flows: After completing Form I-9 as usual, you’ll create an E-Verify case by entering your employee’s information into the system. Within seconds, E-Verify compares this data with records from DHS and SSA. Most of the time, you’ll see an immediate “Employment Authorized” status, and you’re done!
Sometimes, though, the system issues what’s called a Tentative Nonconfirmation (TNC). Don’t panic if this happens. A TNC doesn’t mean your employee isn’t authorized to work. It simply means there’s a data mismatch that needs to be resolved. Your employee has the right to contest a TNC, and you must give them that opportunity.
Remember to record the E-Verify case number on your employee’s Form I-9 or print and file the case details. This documentation is crucial for maintaining compliance. For a deeper dive into integrating these systems effectively, our E-Verify and I-9 Compliance guide has you covered.
New Alternative & Remote Verification Procedures
The world of employment eligibility verification has evolved dramatically, especially as remote work became the norm rather than the exception. Recognizing this shift, DHS introduced game-changing flexibilities that bring verification into the modern age.
Since August 1, 2023, qualifying E-Verify employers can conduct document examination through live video call interactions. This means you can hire someone in another state and still properly verify their eligibility without requiring them to visit a local office or find an authorized representative.
To use this alternative procedure, your business must be enrolled in E-Verify and in good standing with the system. During the verification, you’ll conduct a live video interaction with your employee to review their documents, then annotate the Form I-9 to show you used the alternative procedure.
This flexibility also covers documents that were examined remotely during the COVID-19 period between March 20, 2020, and July 31, 2023. If you used those temporary flexibilities, you’re now on solid ground with permanent procedures.
These changes represent a significant step toward modernizing verification while maintaining security standards. Remote verification acknowledges how we actually work today while ensuring compliance remains strong. For detailed guidance on implementing these procedures, explore our resources on USCIS I-9 Remote Verification and the I-9 Verification Process for Remote Employees.
Staying Compliant: Penalties, Record-Keeping, and Resources
Let’s be honest about something: employment eligibility verification compliance isn’t just a good idea, it’s absolutely essential. The government takes this seriously, and employers who don’t follow the rules face real consequences that can hurt both their wallet and their reputation.
When it comes to penalties, we’re not talking about a slap on the wrist. Fines for Form I-9 violations can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars per form, depending on how serious the violation is. Maybe you forgot to complete Section 2 within three business days, or perhaps you accepted documents that weren’t on the acceptable list. Each mistake adds up quickly.
But money isn’t the only concern. Non-compliance can trigger government audits, which means officials will want to examine all your I-9 records. During these audits, they’ll look for patterns of violations, incomplete forms, or missing documentation. In severe cases where there’s intentional disregard for the law, employers might even face criminal charges.
Record-keeping is your best defense against these problems. You must store completed Form I-9s for three years after the employee’s hire date or one year after they leave, whichever comes later. These records need to be readily available when government officials from DHS, the Department of Labor, or the Department of Justice come knocking.
The key is being proactive rather than reactive. Understanding the risks and having proper systems in place protects your business from costly mistakes. That’s why we’ve developed comprehensive resources on I-9 Compliance Penalties and offer complete Workplace Compliance Solutions to keep you on the right track.
Where to Find Official Information
Navigating employment eligibility verification rules doesn’t have to feel overwhelming when you know where to look for reliable information. The government provides excellent resources, and we always recommend going straight to the source for the most current guidance.
USCIS I-9 Central is your primary destination for everything related to Form I-9 and E-Verify. This comprehensive website houses the latest forms, detailed instructions, news updates, and answers to frequently asked questions. Whenever you have doubts about procedures or need the most current version of any document, Visit I-9 Central for official guidance.
The Handbook for Employers (M-274) deserves a permanent bookmark in your browser. This detailed guide walks you through every step of completing Form I-9, provides examples of acceptable documents, and addresses common scenarios you’ll encounter. Think of it as your compliance bible.
Don’t overlook the Federal Register for official announcements. This is where DHS publishes important changes to employment eligibility verification procedures. Recent updates about remote verification options and document examination procedures appeared here first.
For E-Verify specific questions, E-Verify.gov offers targeted information about enrollment, system operations, and troubleshooting. The site includes helpful tutorials and step-by-step guides for new users.
Free training opportunities are available regularly through USCIS webinars. These sessions let you ask questions directly to government experts and stay updated on policy changes. You can Register for an E-Verify Overview Webinar to expand your knowledge and confidence.
Having these official resources at your fingertips helps ensure you’re always working with accurate, up-to-date information. When compliance questions arise, and they will, you’ll know exactly where to find reliable answers.
Frequently Asked Questions about Employment Eligibility Verification
When it comes to employment eligibility verification, we hear the same questions over and over from employers who want to get it right. Let’s clear up some of the most common confusion points that trip people up.
Does E-Verify replace the Form I-9?
This might be the biggest myth we encounter! No, E-Verify absolutely does not replace Form I-9. Think of them as dance partners, not competitors. Every employer participating in E-Verify must still complete Form I-9 for each new hire, just like everyone else.
Here’s how they work together: E-Verify takes the information you’ve already collected on Form I-9 and runs it through government databases to double-check everything matches up. It’s like having a second pair of eyes review your work. E-Verify confirms the I-9 data against records from the Department of Homeland Security and Social Security Administration, but it can’t do its job without that completed Form I-9 as the starting point.
Both are required for employers who participate in E-Verify. One doesn’t replace the other, they complement each other perfectly.
How long must employers keep Form I-9s?
The retention rules for employment eligibility verification records follow a simple “whichever is later” formula. You must keep each completed Form I-9 for three years after the date of hire, or one year after employment ends, whichever comes later.
Let’s make this crystal clear with real examples. Say you hire someone who stays for just six months. You’d keep their Form I-9 for three full years from their hire date because that’s longer than one year past termination. But if someone works for you for eight years, you’d keep their form for one year after they leave, since that period extends beyond the three-year mark.
This retention period ensures you have records available if government officials conduct an audit. Missing or destroyed forms can lead to penalties, so proper record-keeping isn’t just good practice, it’s financial protection.
Can I use a Spanish version of the Form I-9?
The English version is the official Form I-9 for employment eligibility verification throughout the United States. However, there’s one important exception and one helpful accommodation to know about.
Puerto Rico employers can use the Spanish-language Form I-9 as their official version instead of completing the English form. This makes sense given Puerto Rico’s unique linguistic situation.
For employers everywhere else in the U.S., the Spanish version serves as a translation tool only. You can absolutely use it to help Spanish-speaking employees understand what’s being asked of them, but you’ll still need to complete and file the official English version. Think of the Spanish form as a helpful guide that walks employees through the process in their preferred language, but the English form remains your legal document.
This approach respects language preferences while maintaining standardized record-keeping across the country. It’s a practical solution that helps everyone succeed in the verification process.
Simplify Your Compliance Journey
Let’s be honest – managing employment eligibility verification shouldn’t feel like solving a puzzle every time you hire someone new. Between keeping track of deadlines, understanding document requirements, and staying current with E-Verify changes, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. You started your business to serve customers, not to become an expert in federal compliance regulations.
The verification process involves multiple moving parts that can trip up even experienced HR professionals. There are legal requirements that must be met precisely, administrative burden that eats into productive time, and the constant worry about making costly mistakes. One small error on a Form I-9 or a missed E-Verify deadline can lead to significant penalties during an audit.
This is where expert assistance makes all the difference. At Valley All States Employer Service, we’ve built our entire business around taking the complexity out of workforce eligibility verification. We handle the detailed work of E-Verify processing so you can focus on what matters most – growing your business and serving your customers.
Our team stays current with every regulation change, deadline requirement, and procedural update. We know the ins and outs of remote verification procedures, understand the nuances of document examination, and can spot potential issues before they become compliance problems. When you work with us, you’re not just outsourcing a task – you’re gaining a partner who genuinely cares about keeping your business protected.
Ready to transform your hiring process from stressful to seamless? Our E-Verify Employer Agent Service takes care of all the technical details while you focus on finding great employees. Let’s work together to streamline your workforce eligibility verification today and give you the peace of mind that comes with knowing your compliance is handled by experts.