Why Employer HR Compliance Can Make or Break Your Business
Employer HR compliance is the practice of following all federal, state, and local employment laws that govern how you hire, manage, and treat your employees. It’s not just about avoiding lawsuits, it’s about creating a workplace where people want to work and your business can thrive.
Quick Answer: What Does Employer HR Compliance Include?
- Federal Laws: Title VII, FLSA, ADA, FMLA, OSHA, and others
- State Requirements: Minimum wage, paid leave, pay transparency laws
- Local Ordinances: Ban-the-box, fair scheduling, additional protections
- Documentation: Employee handbooks, posting requirements, record-keeping
- Training: Manager education, harassment prevention, safety protocols
- Audits: Regular self-checks and compliance monitoring
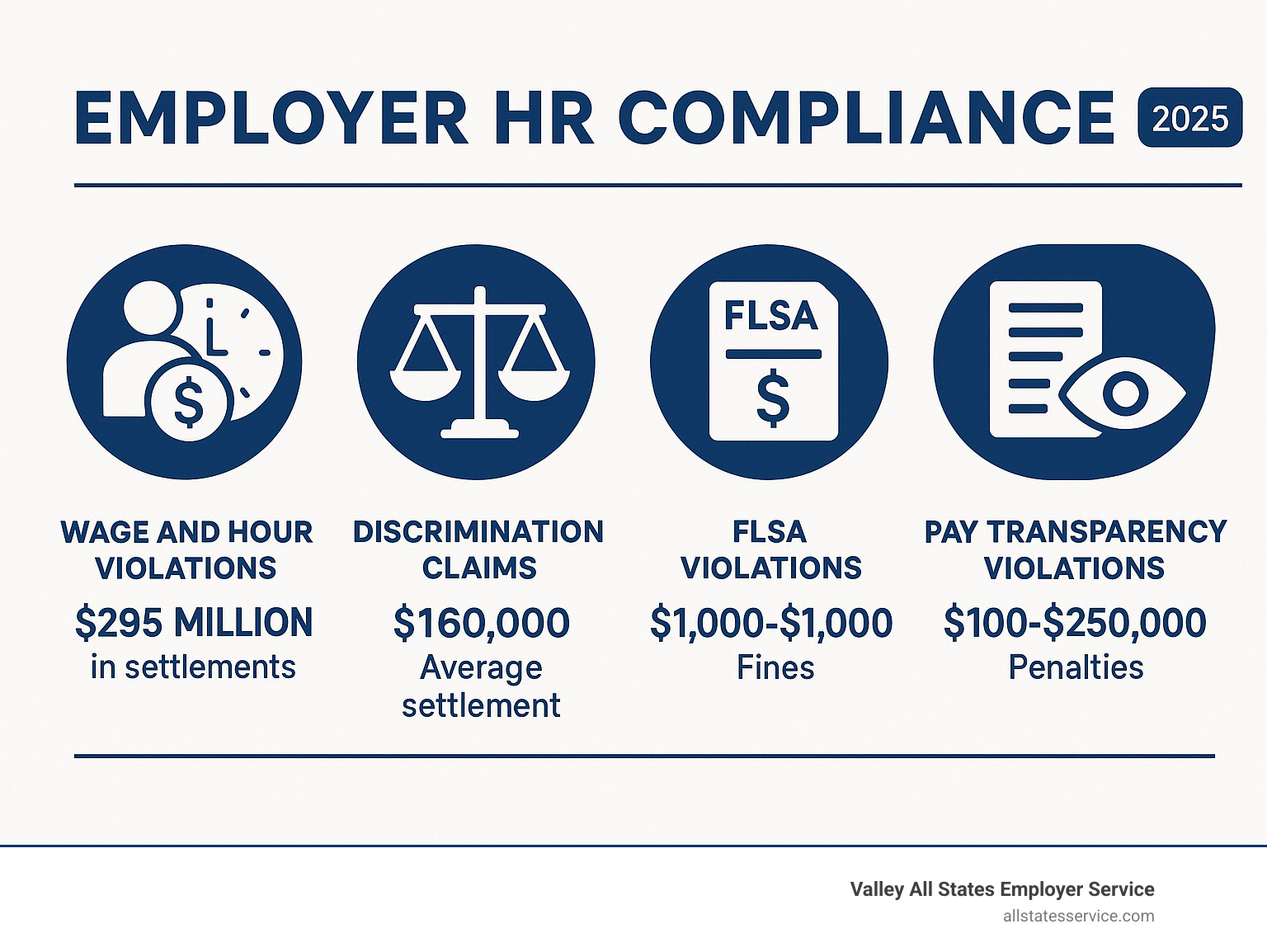
About 50% of business owners say maintaining regulatory compliance is “extremely or very challenging.” The numbers tell the story: wage settlements cost businesses $295 million in 2020. FLSA violations trigger fines from $1,000 to $10,000 per violation. Pay transparency violations range from $100 to $250,000 in penalties. The average employment lawsuit settlement hits $160,000.
But compliance isn’t just about avoiding disaster. Companies that get compliance right attract better talent, reduce turnover, and create cultures where innovation thrives. The challenge? Employment laws change constantly, and if you have remote workers or operate across state lines, you’re juggling multiple sets of rules.
What Is HR Compliance & Why It Matters
Employer HR compliance is your business’s insurance policy against legal disasters. It’s the systematic approach to following employment laws that protect both your company and your employees.
At its core, HR compliance creates the framework for fair treatment, workplace safety, and equal opportunity. Federal laws like Title VII prohibit discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, and national origin. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) governs minimum wage and overtime. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) requires reasonable accommodations for qualified employees with disabilities.
But federal laws are just the foundation. States and local jurisdictions add requirements. California has strict meal and rest break rules. New York City requires bias audits for AI hiring tools. Colorado mandates salary ranges in job postings.
Enforcement agencies aren’t sleeping either. During the first half of 2024, unfair labor practice charges filed with the National Labor Relations Board increased 7% compared to the previous year.
The Cost of Ignoring Employer HR compliance
Direct costs hit hard. FLSA violations cost between $1,000 and $10,000 per violation, with potential imprisonment for willful violations. Pay transparency law violations range from $100 fines to $250,000 penalties. OSHA violations can trigger fines up to $15,625 per violation.
Hidden costs often hurt more. When the EEOC investigates a discrimination charge, your HR team spends months gathering documents and preparing responses. Legal fees pile up quickly. The average employment lawsuit settlement of $160,000 doesn’t include attorney fees, which can easily double that amount.
Employee turnover accelerates when compliance fails. High turnover costs range from 50% to 200% of an employee’s annual salary. Your reputation takes a beating too, making it harder to attract top talent.
How Compliance Builds a Competitive Edge
Smart employers use compliance as a strategic advantage. Top talent gravitates toward compliant employers. Companies with 30% more women in C-suite positions show 15% higher profitability. Workers who trust their employer’s commitment to fair treatment are 81% more likely to report career satisfaction.
When you build robust compliance processes, you’re also building better HR systems overall. Clear policies reduce confusion. Consistent training improves manager effectiveness. Good documentation helps with performance management.

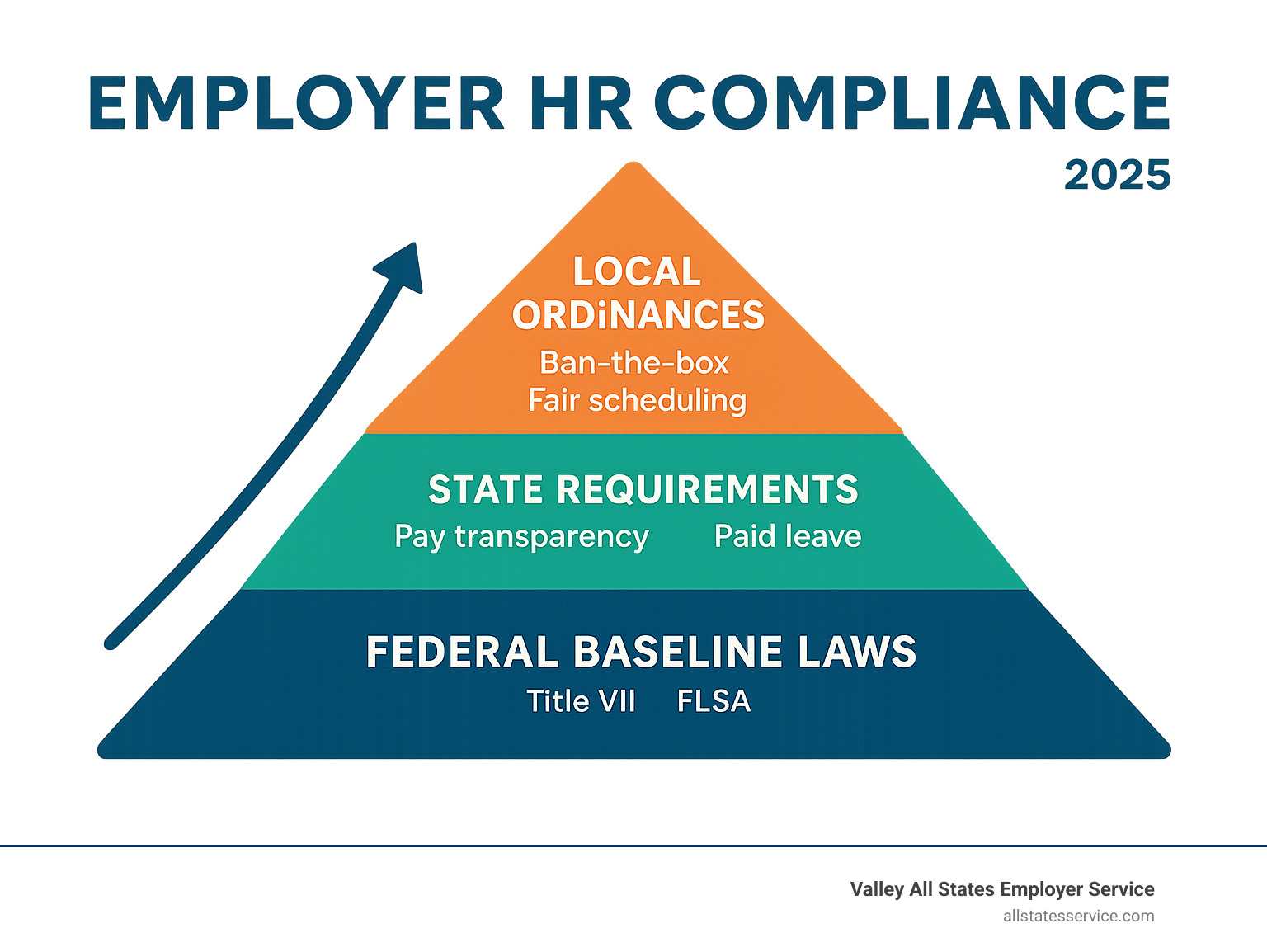
The Legal Landscape: Federal, State & Local Must-Follow Rules
Employer HR compliance is like navigating a three-story building where each floor adds more rules. Federal laws create your foundation. State laws add requirements on the second floor. Local ordinances pile on even more rules at the top.
Federal laws set the baseline. Title VII stops discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, and national origin. The Fair Labor Standards Act keeps minimum wage at $7.25 per hour and requires overtime pay after 40 hours per week. The Americans with Disabilities Act ensures qualified employees with disabilities get reasonable accommodations.
The federal landscape keeps shifting. The Pregnant Workers Fairness Act (PWFA) started changing the game in June 2023. It requires reasonable accommodations for pregnancy, childbirth, and related medical conditions. The final rule on PWFA includes “predictable assessments” like allowing water bottles, flexible schedules, and modified duties.
Immigration compliance hits every employer. The Immigration and Nationality Act requires Form I-9 completion for every employee to verify work authorization. The I-9 forms and guidance were updated with a new form dated January 20, 2025. Violations can cost up to $30,000 per violation.
State laws often exceed federal requirements. While the federal minimum wage sits at $7.25 per hour, many states set much higher rates. Nearly one-third of states have their own paid sick leave laws.
Pay transparency laws are spreading rapidly. More than one-quarter of U.S. employees now have wage transparency law protections, expected to reach 50% in the next few years. These laws require salary ranges in job postings and sometimes annual pay data reporting.
Local ordinances add their own requirements. Cities and counties create employment rules that can catch you off guard. Philadelphia banned pre-employment marijuana testing. Baltimore prohibits certain facial recognition technologies in hiring.
Federal vs State Obligations Comparison
| Area | Federal Baseline | Common State Add-ons |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Wage | $7.25/hour | $15-20/hour in many states |
| Paid Leave | FMLA (unpaid) | Paid sick leave, family leave |
| Pay Transparency | None | Salary ranges in job postings |
| Background Checks | FCRA requirements | Ban-the-box, clean slate laws |
| Discrimination | Title VII protected classes | LGBTQ+, marijuana use, appearance |
| Workplace Safety | OSHA standards | Additional chemical restrictions |
Staying Current With Ever-Changing Regulations
Subscribe to key sources. The Department of Labor sends email updates about new regulations. SHRM provides regular compliance alerts. The EEOC publishes enforcement guidance showing exactly what they’re looking for.
Set up Google Alerts for “employment law,” “HR compliance,” and “workplace regulations” plus your state name. Join professional associations in your area for compliance training and networking. Work with legal counsel before problems arise with quarterly check-ins to review policy updates.
Use compliance software strategically. HR platforms can track regulatory changes and update policies automatically. At Valley All States Employer Service, we specialize in E-Verify compliance, taking that burden off your plate so you can focus on other compliance priorities.
Employer HR Compliance Landmines in 2024-2025
The employer HR compliance landscape feels like a minefield right now. New regulations keep popping up that can turn your carefully crafted policies upside down.
Pay transparency laws are spreading rapidly. More than one-quarter of U.S. employees are now protected by wage transparency laws, expected to hit 50% in the next few years. These aren’t just about posting salary ranges anymore. Some states require detailed pay stub information and annual reports breaking down pay data by race, ethnicity, sex, and job category. Violations can cost anywhere from $100 to $250,000.
AI bias audits are becoming standard. New York City started requiring annual bias audits for automated employment decision tools, and other cities are following. Illinois banned using AI in employment decisions based on ZIP code data. If you’re using AI tools for hiring, screening, or performance management, you need to understand requirements in every jurisdiction where you operate.
Clean slate laws are automatically wiping criminal records. Minnesota’s clean slate law automatically expunges certain records after up to eight years. Colorado seals civil infractions after four years, misdemeanors after seven, and felonies after ten. Criminal history information you could access last year might not be available today.
Cannabis laws create compliance nightmares. Medical marijuana is legal in 39 states plus DC, while recreational use is legal in 23 states plus DC. Employment protections vary wildly. Some states require non-discrimination against medical users. Others explicitly allow drug-free workplace policies.
PWFA accommodations are expanding beyond expectations. The EEOC filed five PWFA lawsuits in fiscal year 2024. The final rule on PWFA includes “predictable assessments” like allowing water bottles, flexible schedules, and modified duties that are presumed reasonable accommodations.
Captive audience speech restrictions are limiting mandatory meetings. Twelve states have passed captive audience bans making attendance at employer meetings about political or religious matters voluntary rather than mandatory.
Hiring & Classification Pitfalls
Ban-the-box laws are expanding beyond traditional employees. Many jurisdictions now apply criminal history restrictions to independent contractors. More info about background checks shows how these laws are reshaping screening practices.
Employee classification mistakes cost serious money. The IRS and Department of Labor have intensified scrutiny on independent contractor classifications. Misclassification can trigger back-pay obligations, tax penalties, and benefits liability.
Exempt vs. non-exempt status confusion persists. The FLSA salary threshold for exempt employees is set at $58,656 as of January 1, 2025. Salary level is just one piece, you also need to meet the duties test.
Wage, Hour & Leave Hot Spots
Overtime miscalculations happen frequently. Calculating overtime gets complex with shift differentials, bonuses, and alternative work schedules. Remote work adds complications around travel time, on-call periods, and home-to-office commutes.
Remote time tracking creates new challenges. You must track all compensable time, including brief email checks and work-related activities performed at home. Clear policies about what constitutes work time are essential.
State paid leave laws are proliferating. Nearly one-third of states have paid sick leave laws. If you operate in multiple states, you need to track different accrual rates, usage rules, and notice requirements.
Employee Data & Privacy Threats
HIPAA compliance extends beyond healthcare companies. If you provide health insurance or wellness programs, you must protect employee health information. Violations can result in fines up to $1.5 million per incident.
Biometric data laws are expanding rapidly. Illinois, Texas, and other states regulate collection and use of biometric information like fingerprints and facial recognition. If you’re using biometric time clocks or security systems, you need clear policies and employee consent.
Background screening data requires special handling. The Fair Credit Reporting Act requires specific procedures for storing and disposing of background check information.
Multi-State, Remote & Global Teams: Keeping Compliance Consistent
Managing employer HR compliance across multiple jurisdictions feels like juggling flaming torches. Every state, city, and country throws its own rules into the mix.
Remote work turns compliance into a puzzle with moving pieces. When your California employee works from Texas for a month, they don’t leave California’s employment laws behind. That worker still gets California’s strict meal and rest break protections. Meanwhile, if your New York employee works temporarily in Florida, you might suddenly need Florida workers’ compensation coverage.
Tax implications can make your head spin. Some states demand tax withholding if an employee works there for just one day. Others give you breathing room with minimum thresholds.
I-9 verification gets more flexible for remote teams. The I-9 forms and guidance allow virtual document inspection for remote employees. You can examine documents via video call and note “COVID-19” in Section 2 of Form I-9. But you must complete physical verification within three business days of returning to normal operations.
Crafting a Universal Handbook That Works Everywhere
Start with your federal foundation. Build core policies around federal requirements like Title VII, FLSA, ADA, and FMLA. These laws apply everywhere and give you solid ground for anti-discrimination, wage and hour, accommodation, and leave policies.
Layer in state-specific requirements. Create addendums for each state where you have employees. California needs meal and rest break policies. New York requires sexual harassment prevention training. Illinois has particular notice requirements for biometric data collection.
Write like you’re talking to a friend, not a lawyer. Skip legal jargon that makes employees’ eyes glaze over. Include real examples and scenarios that illustrate key points.
Build your handbook for change. Use digital formats that allow quick revisions. Include version control and effective dates so everyone knows which rules are current.
Address remote work head-on. Include clear policies for home office safety, equipment use, data security, and time tracking. Spell out which state’s laws apply to remote workers.
Training Managers on Distributed Compliance
Tailor training to what managers actually do. A hiring manager needs different compliance knowledge than a payroll supervisor. Use real-world scenarios that mirror their actual responsibilities.
Break complex topics into bite-sized pieces. A 15-minute module on FMLA basics works better than a two-hour marathon. Micro-learning approaches help managers absorb complex requirements without overwhelming them.
Create quick reference tools for when panic strikes. Develop checklists, flowcharts, and decision trees for common situations. Include contact information for getting help with complex issues.
Schedule regular refresher training. Quarterly compliance updates keep managers current on new requirements. Focus each session on recent changes rather than rehashing basic information.
A learning platform option can help deliver targeted content when managers need it most, making compliance training more effective and less disruptive.
Building & Sustaining a Culture of Compliance
Compliance isn’t just about policies and procedures. It’s about creating a workplace culture where doing the right thing is the default choice.
Leadership sets the tone. When executives demonstrate commitment to compliance, employees follow suit. Leaders need to model ethical behavior, support compliance initiatives, and hold people accountable for violations.
Make compliance everyone’s responsibility. Don’t let compliance become “HR’s job.” Every manager and employee has a role. Build compliance expectations into job descriptions, performance reviews, and recognition programs.
Create safe reporting channels. Employees need ways to report compliance concerns without fear of retaliation. This might include anonymous hotlines, ombudsman programs, or open-door policies.
Respond quickly to compliance issues. When violations occur, swift action demonstrates your commitment. Investigate thoroughly, take corrective action, and communicate the resolution appropriately.
Celebrate compliance successes. Recognize teams and individuals who demonstrate strong compliance practices. Make compliance a source of pride, not just a burden.
Best Practices for Documentation & Communication
Use signed acknowledgments for key policies. When employees receive handbooks, policy updates, or compliance training, get written acknowledgment. Digital signatures work fine, but document the date, version, and method of delivery.
Maintain version control for all policies. Track when policies were updated, what changed, and who approved changes. Keep old versions for reference, but ensure employees always have access to current policies.
Create audit trails for compliance activities. Document training completion, policy acknowledgments, accommodation requests, and disciplinary actions. Good records help demonstrate compliance efforts and protect against false claims.
Communicate changes clearly and promptly. When laws change or policies update, tell employees quickly. Use multiple communication channels and explain why changes are happening.
Make policies easily accessible. Use employee portals, mobile apps, or shared drives to ensure policies are available 24/7. Include search functionality to help people find specific information quickly.
Continuous Audits & Self-Checks
Conduct quarterly spot checks. Pick different compliance areas each quarter and review them thoroughly. Rotate through different areas to maintain comprehensive coverage.
Schedule annual comprehensive audits. Once a year, review all major compliance areas. Use outside counsel or consultants for objective perspectives.
Track key compliance metrics. Monitor indicators like training completion rates, accommodation requests, complaint resolution times, and policy acknowledgment rates.
Benchmark against industry standards. Compare your practices to similar organizations. Industry associations often provide benchmarking data and best practices.
Document audit findings and corrective actions. Keep records of what you found, what you fixed, and when you fixed it. This documentation proves your good faith compliance efforts.

When Things Go Wrong: Investigations, Audits & Lawsuits
Nobody plans for employer HR compliance disasters, but they happen even to well-intentioned businesses. When that call comes in from the EEOC or DOL, your response in the first few hours can determine whether you’re dealing with a manageable problem or a company-threatening crisis.
EEOC charges require immediate attention. When the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission sends you a discrimination charge, you typically have 30 days to respond. Start gathering relevant documents immediately. Interview witnesses while memories are fresh. Your position statement needs to be comprehensive and accurate.
DOL audits can feel like surprise inspections. The Department of Labor doesn’t always give advance warning. Designate one person as your point of contact to prevent mixed messages. Provide exactly what they request, nothing more, nothing less.
Document preservation becomes critical overnight. The moment investigations or lawsuits begin, implement litigation holds immediately. Preserve emails, text messages, personnel files, and electronic records. Destroying documents after legal proceedings start can result in penalties worse than your original violation.
Immediate Steps After Finding a Violation
Stop the violating practice right now. If you find wage and hour violations, fix your payroll practices immediately. Don’t wait for legal advice to stop harmful practices. Every day you continue a violation makes the problem worse.
Preserve everything, even the embarrassing stuff. Secure all documents, emails, and records related to the violation. Complete preservation protects you from spoliation claims and ensures thorough investigation.
Get legal counsel involved early. Employment attorneys can advise on disclosure obligations, corrective actions, and damage control strategies. Early legal involvement often prevents small problems from becoming large ones.
Conduct your own thorough investigation. Determine the scope of the violation and identify all affected employees. Calculate potential damages so you know what you’re facing.
Develop specific corrective action plans. Create concrete steps to prevent recurring violations. This might include policy updates, training programs, system changes, or personnel actions.
Cooperating With Agencies Without Making It Worse
Choose your spokesperson carefully. Designate one person to communicate with investigators to prevent conflicting statements. Usually, this should be someone with legal training or working closely with legal counsel.
Complete and accurate information is non-negotiable. Incomplete or misleading responses can turn routine investigations into major problems. If you don’t know something, say so honestly.
Meet every deadline and commitment. When you promise to provide documents by a certain date, deliver on time. Missed deadlines suggest lack of cooperation and can result in additional penalties.
Document every interaction with investigators. Keep detailed records of meetings, phone calls, and correspondence. This helps track commitments and provides evidence of your cooperation efforts.
Consider settlement opportunities seriously. Many investigations can be resolved through settlement agreements. Settlement often costs less than prolonged litigation and allows you to control the outcome.
The key to surviving compliance crises is responding quickly, honestly, and strategically. While we can’t prevent every compliance problem, we can help you avoid E-Verify headaches so you can focus your energy on other compliance challenges.
Frequently Asked Questions about Employer HR Compliance
What employee notices and posters are required?
Federal law requires several workplace postings displayed where employees can easily see them. The Department of Labor provides a comprehensive poster covering Fair Labor Standards Act, OSHA safety requirements, Family and Medical Leave Act, and other federal requirements. The EEOC adds its own anti-discrimination notices.
State and local governments add their own posting requirements. California employers need paid sick leave notices. New York requires specific sexual harassment prevention information. Some cities have their own minimum wage or fair scheduling posters.
Electronic posting works in some situations, but most workplaces still need physical posters. Remote workers need access to required notices through employee portals or email distribution. Check with your state labor department for specific requirements.
How do we handle ADA or PWFA accommodation requests?
Both the Americans with Disabilities Act and Pregnant Workers Fairness Act require an “interactive process.” Think of it as a conversation, not a legal proceeding.
Start the conversation immediately when an employee mentions needing help with job duties. Don’t wait for formal paperwork. The moment someone says “I’m having trouble with…” you’re in accommodation territory.
Focus on solutions, not diagnoses. You don’t need intimate details of someone’s medical condition. Discuss what they need to perform essential job functions and what specific barriers they’re facing.
The PWFA makes some accommodations presumptively reasonable. These “predictable assessments” include allowing water bottles at workstations, providing flexible schedules for medical appointments, and modifying duties temporarily.
Document everything thoroughly. Keep records of all accommodation discussions, decisions, and implementations. This helps track what works and assists if the employee’s needs change over time.
What resources help small teams stay compliant on a budget?
Government agencies want to help you succeed. The Department of Labor, EEOC, and OSHA provide free compliance assistance including phone consultations, on-site visits, and educational materials.
Industry associations provide incredible value. Trade associations offer compliance resources, training sessions, and group purchasing power for legal services. Annual membership fees usually pay for themselves through compliance support.
Technology can level the playing field. HR software platforms automate many compliance tasks like policy updates, training tracking, and document management. Many offer small business pricing.
Outsource your biggest headaches. Focus on high-risk areas. Payroll companies handle tax compliance. Benefits administrators manage COBRA and HIPAA requirements. For E-Verify processing, we handle verification for employers, reducing errors and administrative burden so you can focus on running your business.
Invest in manager training. Well-trained supervisors make fewer compliance mistakes. Online training programs cost much less than legal problems and help prevent violations before they occur.
Build relationships with employment attorneys before you need them. Many law firms offer small business retainer programs providing ongoing advice at predictable monthly costs.
Conclusion
Employer HR compliance doesn’t have to keep you up at night. When you approach compliance strategically, it transforms from a necessary evil into a genuine business advantage.
While your competitors scramble to fix compliance problems after they happen, you’re building systems that prevent issues before they start. You’re creating the kind of workplace that attracts top talent and keeps good people around. You’re protecting your business from costly lawsuits and regulatory penalties.
The secret isn’t trying to become a compliance expert overnight. It’s about building smart systems that work for your specific situation. Start with rock-solid policies covering federal, state, and local requirements that actually apply to your business. Train your managers so they can spot potential problems early. Create processes for staying current with the laws that matter most to your industry.
You don’t have to handle everything yourself. Smart business owners focus their energy where it makes the biggest impact and get help with the specialized stuff.
That’s exactly where Valley All States Employer Service comes in. We handle E-Verify workforce eligibility verification so you don’t have to worry about one of the trickiest parts of employment compliance. Our team knows the ins and outs of E-Verify processing, which means fewer errors, less administrative headache, and more time for you to focus on what you do best.
Compliance isn’t just about avoiding problems. It’s about creating workplaces where people actually want to work, where innovation happens naturally, and where your business can grow without constantly looking over your shoulder.
Ready to take E-Verify off your plate? Contact our team today to learn how we can streamline your workforce verification processes and reduce your compliance risks. More info about our HR compliance checklist gives you additional resources for building a comprehensive compliance program that actually works.
Don’t wait for compliance problems to find you. Take control today.